Thermal and mechanical properties of azomethine functionalized cyanate ester/epoxy blends
Abstract
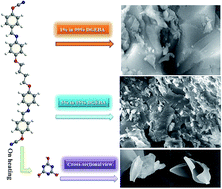
A series of azomethine functionalized diols were synthesized by the condensation reaction of aromatic diamines with 4-hydroxy benzaldehyde. Aromatic diamines with different alkyl chain lengths have been used to prepare the bisphenols. These bisphenols were converted to their corresponding cyanate esters by treating with cyanogen bromide (CNBr) in the presence of triethyl amine (Et3N). The curing temperature was measured using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The maximum curing temperatures of these cyanate esters are in the range of 203–242 °C. Thermal properties of the cured cyanate esters were studied by using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The polymers showed excellent thermal stability (T5% was found to be in the range of 358 to 465 °C and T10% was found to be in the range of 508 to 525 °C) and the percentage of char yield at 800 °C was found to be in the range of 37.06 to 57.26. The flame retardancy of the cyanate ester resins was evaluated using the limiting oxygen index value which is in the range of 32.32 to 40.40 at 800 °C. Cyanate ester/epoxy blends were prepared and the morphology of the blends were studied by scanning electron microscopy. The mechanical properties and glass transition temperature of cyanate/epoxy ester blends was studied using dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) and the Tg was found to increase with increasing cyanate ester content (1 to 5%).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...