Supramolecular, prodrug-based micelles with enzyme-regulated release behavior for controlled drug delivery
Abstract
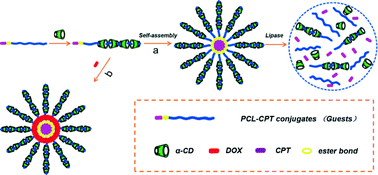
Supramolecular polymer micelles (SMPMs) engineered by the host–guest interaction of α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) and poly(ε-capralactone) (PCL) homopolymer have been recently reported as robust drug delivery systems. The incorporation of supramolecular chemistry affords significantly obvious advantages of convenience in fabrication and controllability in properties, in contrast to conventional micelles. This work aims to design and develop novel SMPMs assembled by the anticancer drug camptothecin carrying PCL (CPT-PCL) and α-CD. The prodrug strategy developed not only can introduce the steric effect to facilitate the supramolecular nano-assembly but also can provide the capability to prevent the premature release as well as to regulate the drug release by enzymes. The CPT drug and PCL polymer were chemically bonded through an ester bond linkage hydrolyzable in the presence of lipase. The resultant SMPMs were spherical with a hydrodynamic size of around 220 nm and a fixed drug ratio dependent on the molecular weight of PCL employed. The enzyme-induced drug release behavior and cytotoxicity of CPT-carrying SMPMs were further evaluated, and the results revealed the promising application of these micelles for controlled drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...