Integrative analysis of lung development–cancer expression associations reveals the roles of signatures with inverse expression patterns†
Abstract
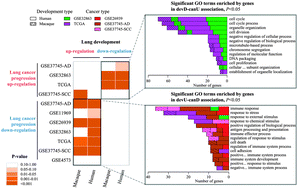
Recent studies have focused on exploring the associations between organ development and malignant tumors; however, the clinical relevance of the development signatures was inadequately addressed in lung cancer. In this study, we explored the associations between lung development and lung cancer progression by analyzing a total of two development and seven cancer datasets. We identified representative expression patterns (continuously up- and down-regulated) from development and cancer profiles, and inverse pattern associations were observed at both the gene and functional levels. Furthermore, we dissected the biological processes dominating the associations, and found that proliferation and immunity were respectively involved in the two inverse development-cancer expression patterns. Through sub-pathway analysis of the signatures with inverse expression patterns, we finally identified a 13-gene risk signature from the cell cycle sub-pathway, and evaluated its predictive performance for lung cancer patient clinical outcome using independent cohorts. Our findings indicated that the integrative analysis of development and cancer expression patterns provided a framework for identifying effective molecular signatures for clinical utility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...