Beyond the flavour: a de-flavoured polyphenol rich extract of clove buds (Syzygium aromaticum L) as a novel dietary antioxidant ingredient
Abstract
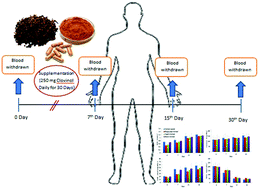
Though kitchen spices constitute an important source of dietary antioxidants, their consumption at a physiologically relevant dose is very often hampered by their unpleasant flavour characteristics. The present paper describes a novel approach to derive stable de-flavoured spice extracts with minimised taste and odour profiles which are suitable for impregnation into a variety of food and beverage matrices at physiologically relevant doses. A popular kitchen spice, clove bud (Syzygium aromaticum L), having strong flavour and pungency characteristics was selected in the present study to derive a de-flavoured extract with a standardised polyphenolic profile (Clovinol) and was incorporated into various foods. The antioxidant efficacy of Clovinol on healthy human volunteers who check and answer official emails involving responsibility was investigated by analysing their endogenous antioxidant enzymes and the extent of lipid peroxidation upon consumption of Clovinol either as capsules or in a different food/beverage at 250 mg per serving per day for 30 days. It was observed that Clovinol can be conveniently incorporated in various food matrices without flavour issues and the consumption of such food/beverage items may support an effective detoxification process with an average elevation of 33 ± 3% in catalase, 66 ± 8% in SOD, 56 ± 5% in GPx and 167 ± 21% in GSH levels, and 81 ± 11% attenuation in membrane lipid peroxidation level.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...