Thioiminium and thiaphospholanium derived from acetonitrile via nickel(ii)–(2-mercaptophenyl)phosphine complexation†
Abstract
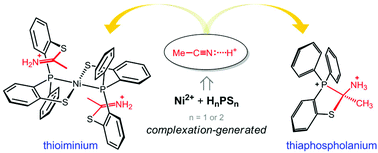
[Ni(P(o-C6H4S)(o-C6H4SC(CH3)![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH2)(C6H5))2](ClO4)2 (2) with two thioiminium functionalities is derived from CH3CN solvent under anhydrous conditions. Moreover, thiaphospholanium salts, [(C6H5)P(C6H4SC(CH3)(NHCOCH3))(o-C6H4SH)](ClO4) (3) and [(C6H5)2-P(C6H4SC(CH3)(NH3))](ClO4)2 (5), can be obtained through a similar Pinner-type nitrile activation. These results demonstrate the possible intermediate of enzymatic nitrile transformation and also provide an approach to the preparation of 2-amino-1,3-benzothiaphospholanium derivatives.
NH2)(C6H5))2](ClO4)2 (2) with two thioiminium functionalities is derived from CH3CN solvent under anhydrous conditions. Moreover, thiaphospholanium salts, [(C6H5)P(C6H4SC(CH3)(NHCOCH3))(o-C6H4SH)](ClO4) (3) and [(C6H5)2-P(C6H4SC(CH3)(NH3))](ClO4)2 (5), can be obtained through a similar Pinner-type nitrile activation. These results demonstrate the possible intermediate of enzymatic nitrile transformation and also provide an approach to the preparation of 2-amino-1,3-benzothiaphospholanium derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...