Synthesis and characterisation of lanthanide-hydroporphyrin dyads†
Abstract
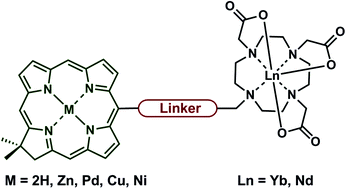
Fluorescence spectroscopy is in many ways the ideal tool for the interrogation of complex biological systems, as it is non-invasive, sensitive, and offers high spatiotemporal resolution. For biomedical imaging luminescent probes absorbing and emitting in the red-to-near infrared (NIR) region are best suited to maximise tissue penetration and minimise damage to cellular components. NIR-emitting lanthanides (Ln) sensitised with red-absorbing antennae are promising candidates for these applications, assuming the challenges of poor photophysical properties and tedious syntheses of the complexes are overcome. Chlorins are porphyrin-type tetrapyrroles with intense red absorption. Recently chlorins have been shown to sensitise Yb and Nd emission when incorporated into Ln-complexes. Here we expand on our previous work, and explore the effect of chlorin structure, metallation state, chlorin–Ln-complex linker length and mode of attachment on the properties of chlorin–Ln complexes. As chlorin absorption bands are ∼20 nm fwhm and readily tunable, a deeper understanding of structure–property relationships would enable the use of chlorin–Ln complexes in multicolour imaging using antenna-specific excitation. A detailed description of antenna and complex syntheses and photophysical characterisation is given. A number of challenges were identified, which will have to be addressed in future studies to enable multicolour imaging using the NIR-emitting lanthanides.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dalton Discussion 14: Advancing the chemistry of the f-elements

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...