A combination of positive dielectrophoresis driven on-line enrichment and aptamer-fluorescent silica nanoparticle label for rapid and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus†
Abstract
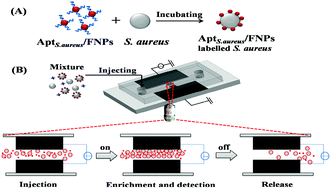
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is an important human pathogen that causes several diseases ranging from superficial skin infections to life-threatening diseases. Here, a method combining positive dielectrophoresis (pDEP) driven on-line enrichment and aptamer-fluorescent silica nanoparticle label has been developed for the rapid and sensitive detection of S. aureus in microfluidic channels. An aptamer, having high affinity to S. aureus, is used as the molecular recognition tool and immobilized onto chloropropyl functionalized fluorescent silica nanoparticles through a click chemistry approach to obtain S. aureus aptamer–nanoparticle bioconjugates (AptS.aureus/FNPs). The pDEP driven on-line enrichment technology was used for accumulating the AptS.aureus/FNP labeled S. aureus. After incubating with S. aureus, the mixture of AptS.aureus/FNP labeled S. aureus and AptS.aureus/FNPs was directly introduced into the pDEP-based microfluidic system. By applying an AC voltage in a pDEP frequency region, the AptS.aureus/FNP labelled S. aureus moved to the electrodes and accumulated in the electrode gap, while the free AptS.aureus/FNPs flowed away. The signal that came from the AptS.aureus/FNP labelled S. aureus in the focused detection areas was then detected. Profiting from the specificity of aptamer, signal amplification of FNP label and pDEP on-line enrichment, this assay can detect as low as 93 and 270 cfu mL−1S. aureus in deionized water and spiked water samples, respectively, with higher sensitivities than our previously reported AptS.aureus/FNP based flow cytometry. Moreover, without the need for separation and washing steps usually required for FNP label involved bioassays, the total assay time including sample pretreatment was within 2 h.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...