Elucidating the interaction of γ-hydroxymethyl-γ-butyrolactone substituents with model membranes and protein kinase C–C1 domains†
Abstract
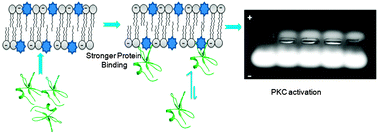
The protein kinase C (PKC) family of proteins is an attractive drug target. Dysregulation of PKC-dependent signalling pathways is related to several human diseases like cancer, immunological and other diseases. We approached the problem of altering PKC activities by developing C1 domain-based PKC ligands. In this report γ-hydroxymethyl-γ-butyrolactone (HGL) substituents were investigated in an effort to develop small molecule-based PKC regulators with higher specificity for C1 domain than the endogenous diacylglycerols (DAGs). Extensive analysis of membrane–ligands interaction measurements revealed that the membrane-active compounds strongly interact with the lipid bilayers and the hydrophilic parts of compounds localize at the bilayer/water interface. The pharmacophores like hydroxymethyl, carbonyl groups and acyl-chain length of the compounds are crucial for their interaction with the C1 domain proteins. The potent compounds showed more than 17-fold stronger binding affinity for the C1 domains than DAG under similar experimental conditions. Nonradioactive kinase assay confirmed that these potent compounds have similar or better PKC dependent phosphorylation capabilities than DAG under similar experimental conditions. Hence, our findings reveal that these HGL analogues represent an attractive group of structurally simple C1 domain ligands that can be further structurally altered to improve their potencies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in Molecular BioSystems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...