Black TiO2 nanotube arrays for high-efficiency photoelectrochemical water-splitting†
Abstract
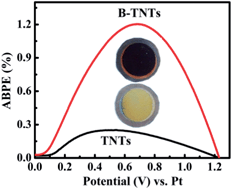
Black titania nanotube arrays are prepared for the first time by the melted aluminium reduction of pristine anodized and air-annealed titania nanotube arrays. The black titania nanotubes with substantial Ti3+ and oxygen vacancies exhibit an excellent photoelectrochemical water-splitting performance due to the improved charge transport and separation and the extended visible light response. An impressive applied bias photon-to-current efficiency of 1.20% is achieved.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 10th Anniversary: Dedicated Authors

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...