Solubilization, dispersion and stabilization of magnetic nanoparticles in water and non-aqueous solvents: recent trends
Boris I. Kharisov
a,
H. V. Rasika Dias
b,
Oxana V. Kharissova
*a,
Alejandro Vázquez
a,
Yolanda Peña
a and
Idalia Gómez
a
aUniversidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Mexico. E-mail: bkhariss@hotmail.com
bDepartment of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, Texas 76019, USA.. E-mail: dias@uta.edu
First published on 28th August 2014
Abstract
Recent achievements in the solubilization and stabilization of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are reviewed. The majority of reported MNPs correspond to iron-based {nZVI, superparamagnetic iron oxides (SPIONs), core–shell Fe/Au or FexOy/Au nanoparticles and ferrites} nanoparticles, with a few numbers corresponding to MnO and cobalt nanoparticles. Magnetic nanoparticles can be solubilized in water or non-aqueous solvents for short or long time periods. The main approaches for MNP solubilization are discussed, namely, suitable choice of precursors, pH, surfactants/coating agents, and solvents, as well as functionalizing agents. MNPs are generally solubilized by functionalization with water-soluble compounds/moieties (in particular, sulfonic acid disodium salts, soluble polymers, porphyrins and calixarenes), under conditions of the thermal decomposition of low stability metal complexes, coprecipitation, microwave heating, and by ultrasonication. The polyol strategy is frequently applied to increase MNP solubility. The stabilization of MNPs in solutions could be achieved with the help of inorganic, monomeric and polymeric compounds.
Introduction
In nanotechnology, one of hottest current topics corresponds to magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) due to their extensive applications in areas such as biomedicine1 (in particular as MRI agents),2 drug delivery,3 and for the remediation of pollutants4 {generally Cr(VI), As(V), Ni(II)}. A series of recent books,5–7 book chapters,8,9 reviews,10–18 and a host of experimental articles have been published since 2000, describing the synthesis and characterization methods, functionalization, peculiarities, and applications of MNPs. Among these, a large majority of recent reports are dedicated to the nanoparticles of elemental iron {“nano zero-valent iron” (nZVI)}, iron oxides {“superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles” (SPIONs)}, core–shell iron (or iron oxide)–gold nanoparticles,19 and, less frequently, for MnO, cobalt nanoparticles,20 and ferrites, for instance functionalized ZnxMn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1) nanoparticles.21 To date, most interest in the clinical applications of MNPs have focused on iron oxide because of the chemical stability, biological compatibility, and relative ease of the manufacture of magnetite (Fe3O4) and maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles.22Magnetic nanoparticles possess distinct “solubilities” in aqueous and non-aqueous solvents, depending on their size and the type of functionalizing molecules. The capacity to be solubilized or dispersed for short or long periods and the stability of MNPs in liquid phases is very important for the abovementioned applications, and hence, considerable efforts have been made to achieve a higher solubility of MNPs, first of all in aqueous media. Highly soluble MNPs have much greater applications in biomedicine; soluble iron oxide MNPs have stronger remediation effects compared to the insoluble ones. When studying changes in the solubility of MNPs, the magnetic interactions23 between them, in particular, should be taken into account, as well as strategies toward nanoseparations24 and magnetic separations.25 In this review, we summarize the recent achievements in the solubilization of MNPs and give an overview on their stabilization in solutions. We note that special investigations on the transformations of “insoluble (already prepared) → water- or organic-soluble MNPs” are rare; instead, generally, researchers synthesize directly soluble NPs.
Definitions of solubilization and dispersion terms in relation to nanoparticles
According to non-nanochemical classic definitions reported in Wikipedia and elsewhere, solubilization (an IUPAC definition26) is a short form for micellar solubilization, a term used in colloidal and surface chemistry. Solubilization may occur in a system consisting of a solvent, an association colloid (i.e., a colloid that forms micelles), and at least one other component called the solubilizate (i.e., the component that undergoes solubilization). Solubilization is distinct from dissolution (the process by which a solute forms a solution in a solvent) because the resulting fluid is a colloidal dispersion. This suspension is distinct from a true solution, and the amount of the solubilizate in the micellar system can be different (often higher) than the regular solubility of the solubilizate in the solvent”. Dispersion is a process by which (in the case of solids' becoming dispersed in a liquid) agglomerated particles are separated from each other and a new interface, between an inner surface of the liquid dispersion medium and the surface of the particles to be dispersed, is generated.27 Dispersion is a much more complicated (and less-understood) process than most people believe.Nanoparticles in solutions present typical colloidal systems, consisting of a continuous phase, which is a dispersed medium (solvent) and a dispersed phase (nanoparticle).28 Such systems with a solid dispersed phase and a liquid dispersed medium are called sols. Colloidal systems in organic solvents are frequently called organosols, while analogous dispersions in water are called hydrosols. A distinctive feature of colloidal solutions is their relatively low stability, which is attributed to their large particle size and perceptible free surface energy. Each nanoparticle appears to be an aggregate of atoms or of more or less simple molecules. Any change in conditions could result in aggregate size variation and precipitate fallout. The stability of colloidal solutions is considered to be one of the key problems of colloidal chemistry. A system is stable when its dispersed phase can exist as separate individual particles for a long time (a few months or even years).28
Applying both terms above (solubilization and dispersion) to nanoparticles and then analyzing the published scientific research articles, it is evident that there is an important issue or misunderstanding between the terms “dispersion” and “solubilization” (in particular, a discussion of these terms related to carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is presented in ref. 29). Many researchers use the terms interchangeably, particularly when stating the interaction of CNTs with liquids, which can cause further confusion. The fundamental question when dealing with carbon nanotubes in liquids, particularly in water, is: are they dissolved or dispersed? It has been suggested that it is more appropriate to use the term “dispersion” rather than “solution”. For other nanoparticles, in particular for magnetic NPs, similar discussions might also appear later.
Nanoparticles have a particular tendency to want to lower their very high surface energy, which is the origin of their thermodynamic instability. Bare nanoparticles tend to stabilize themselves either by the sorption of molecules from the surroundings or by lowering their surface area through coagulation and agglomeration. In order to avoid this, nanoparticles have to be stabilized; the stabilization of NPs30 is a very important aspect in nanochemistry. There are two modes of stability of colloidal solutions.28 Kinetic stability is the stability of the systems relative to gravity forces. Some crucial factors that determine the kinetic stability of colloids are Brownian motion, dispersion, viscosity of the medium, etc. Aggregation stability is the ability of the system to preserve the degree of particle dispersity.28 This type of stability is attributed to the ability of nanoparticles to create large aggregates to adsorb low-molecular ions on their surface from the solution, leading to formation of an adsorption layer.
Overview of the main synthesis techniques for magnetic nanoparticles
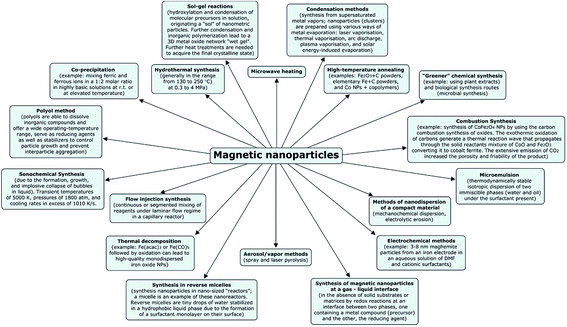
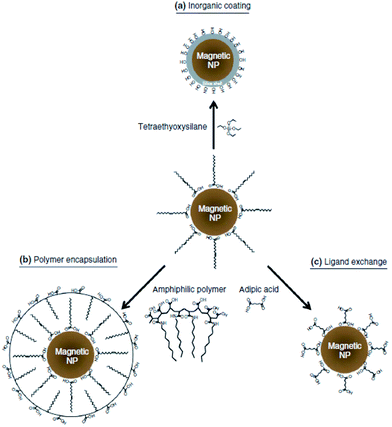
A plethora of techniques are nowadays used for MNP fabrication (Fig. 1). However, not all of them are suitable for obtaining soluble MNPs. Among the techniques, the surface functionalization of MNPs with organic materials31,32 {relatively small molecules (amino acids,33 citric acid salts,34 vitamins,35 cyclodextrin,36 etc.) and surfactants,37 polymers,38,39 biological molecules,40,41 etc.} or with inorganic materials (silica,42,43 metals,44 metal oxides or sulfides45) are the most common in order to obtain soluble MNPs. Other techniques for the preparation of soluble or insoluble MNPs include coprecipitation,46 synthesis in reverse micelles,47 sonolysis,48 electrochemical deposition,49 mechanochemical dispersion,50 solution plasma51 and sol–gel processes,52 arc discharge,53 spray54 and laser55 pyrolysis, flow injection synthesis,56 thermal decomposition,57 hydrothermal,58,59 microwave60 and microwave solvothermal,61 combustion synthesis,62 high-temperature annealing63 and other high temperature syntheses,64 micro-65 and nanoreactors such as protein cages,66 vesicles,67 and microemulsions.68 In terms of the advantages and disadvantages for preparing iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs), regarding their size and morphology control, thermal decomposition by the hydrothermal synthetic route seems to be the optimal method. For obtaining water-soluble and biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs), coprecipitation is often employed, but this method presents low control of the particle shape, and can result in a broad distribution of sizes and aggregation of the particles. Thus, as a time-competitive alternative, the sonochemical route can also be used to synthesize iron oxide NPs with unusual magnetic properties. Among more rare methods, we can mention the “greener” synthesis of α-Fe2O3 NPs using potato as the starch template,69 plant extracts,70 or the use of microorganisms for obtaining Fe3O4 and Fe3S4.71Iron-based nanoparticles and fluids: definitions and solubility
IONPs are the most common MNPs. IONPs functionalized by small molecules or surfactants can be divided into three types: oil-soluble, water-soluble, and amphiphilic.72 Oil-soluble IONPs are functionalized IONPs with chemical groups on the surface that have a weak attraction for the solvent environment (generally hydrophobic group, such as the fatty acid, alkyl phenol (n = 6–10, linear or branched)). Water-soluble IONPs are functionalized IONPs with chemical groups on the surface that have a strong attraction for the solvent environment (generally hydrophilic groups, such as the ammonium salt, polyol, lycine). Amphiphilic IONPs are functionalized IONPs with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic chemical groups on the surface; where, the main chain of these functionalized small molecules or surfactants showed the concurrence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic structural regions, which give the functionalized IONPs both oil-solubility and water solubility.A special form of soluble MNPs are “magnetic fluids”, i.e., stable colloidal systems of fine single-domain magnetic particles (for example, Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, Co, MnFe2O4, etc.) coated with surfactants, and suspended in a liquid carrier, such as water, mineral oil, damping oil, paraffin, kerosene, and so on. The properties of magnetic fluids can be effectively controlled by an external magnetic field, which opens up broad possibilities for technical and biomedical applications.73,74 The most commonly used ferrofluid contains spherical magnetic particles with typical sizes of 10 nm, dispersed in an apolar solvent. Sedimentation of these particles is sufficiently counteracted by Brownian motion to keep them dispersed for years. To prevent aggregation, the colloids can be covered with a thin layer of surfactant, commonly a monolayer of oleic acid (steric repulsion), or the particles can be prevented from sticking to each other by an electrostatic bilayer (electrostatic repulsion), which gives the particles stability in many liquid carriers. They have found wide application in a variety of fields, such as electronic packing, mechanical engineering, aerospace, and bioengineering. One of many unique properties of ferrofluids is their tunable viscosity by an external magnetic field (the so-called magnetoviscous effect).
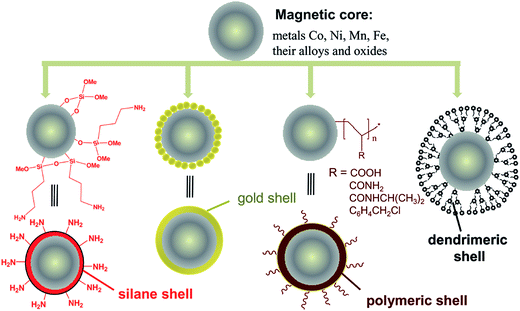
Iron oxide nanoparticles, due to the favorable features they exhibit, are the only type of MNPs approved for clinical use by the Food and Drug Administration.75 Their attributes include facile single step synthesis by the alkaline coprecipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+, chemical stability in physiological conditions, and the possibility of chemical modification by coating the iron oxide cores with various shells, e.g., golden, polymeric, silane, or dendrimeric (Fig. 2). In addition, their extremely low toxicity allows remediation uses based on their the reactions, shown in Fig. 3. In this respect, this is why the nZVI, IONPs, and others (about 15 compounds) are the most frequently used MNPs, and hence why they attract so much attention from researchers.
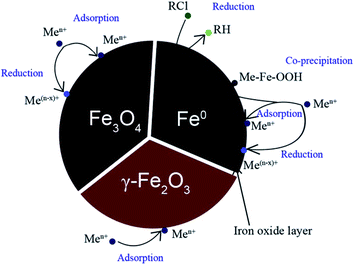 | ||
| Fig. 3 Schematic model of magnetic nanoparticles (nZVI, Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3, Me = metal). The zero-valent iron in the core mainly provides the reducing power for the reactions with contaminants. The oxide shell provides sites for sorption. Adsorption also occurs on the iron oxides (Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3) surface, while Fe3O4 possesses reducing power.76 Reproduced with permission of Elsevier Science {S. C. N. Tang and I. M. C. Lo, Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications, Water Res., 2013, 47(8), 2613–2632}. | ||
Solubilization of MNPs by functionalization
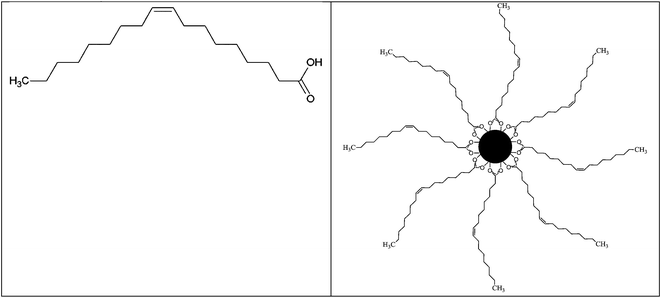
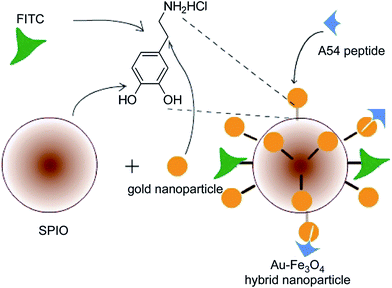
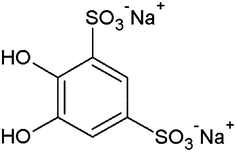
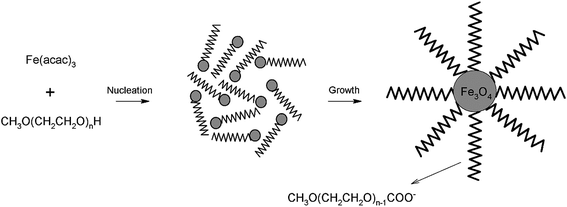
The functionalization of MNPs by a variety of distinct organic compounds is the standard route to increase their solubility. The MNPs, formed by reduction reactions from metal salts, can be functionalized directly or step-by-step by the substitution of the primary coating organic layer by another compound. Among the compounds most widely used in the first step of the functionalization of MNPs, we note oleic acid77 (Fig. 4), sodium oleate,78 and oleylamine.79–82 Oleic acid is frequently used in ferrite nanoparticle synthesis, because it can form a dense protective monolayer, thereby producing highly uniform and monodisperse particles. Generally, MNP composites functionalized with oleic acid are first prepared and then the oleic acid moiety is substituted by other compounds. Due to its long hydrophobic tail, colloidal Fe3O4 NPs prepared using oleic acid are highly soluble in organic solvents, such as toluene, hexane, chloroform, etc.83Among a host of MNPs with functionalizing agents, dopamine (DA)-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs, Fe3O4@DA) were synthesized using a one-step process by a modified coprecipitation method, and then 2–3 nm gold nanoparticles were easily conjugated to Fe3O4@DA nanoparticles by the electrostatic force between the gold nanoparticles and the amino groups of dopamine, to afford water-soluble Au–Fe3O4 hybrid nanoparticles (Fig. 5).84 These formed hybrid nanoparticles show good water solubility and were easily functionalized with a targeted small peptide A54 and the fluorescence probe fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) for liver cancer cell BEL-7402 imaging. In a related report,85 monodisperse, ultrasmall, water dispersible superparamagnetic IONPs were initially synthesized in organic solvents using oleic acid as a dispersant, and then underwent subsequent ligand exchange of oleic acid for dopamine and Tiron (4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonic acid disodium salt) (Fig. 6 and 7), which allowed for superior colloidal stability in aqueous media. Zeta potential measurements confirmed the stability of the nanoparticles upon redispersal in water or biologically relevant buffers. The synthesized particles also retained their general shape, size, and crystallinity after the ligand exchange. This exchange method is quick, consumes minimal reagents, and can be conducted at room temperature, making it an efficient synthetic procedure. Earlier, this ligand exchange process of oleic acid for dopamine was studied in detail.86 Both oleic acid and dopamine are covalently bound to the surface via a chelating bidentate interaction to the iron species. Iron oxide NPs, upon this new functionalization, become more hydrophilic. The origin of the improvement in the magnetic properties of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles upon functionalization was hypothesized to lie in the steric interaction between the surfactant molecules, the oleic acid, and dopamine, and arising from their strongly covalent interaction with the Fe atoms on the oxide NP surface to form a chelating bidentate bond.
1,3-Dialkylimidazolium-based ionic liquids were chemically synthesized and bonded on the surface of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with facile reactions (Fig. 8).87 The solubility of these NPs in organic solvents depends on the alkyl chain length and the anions of the ionic liquids. Moreover, the resulting NPs showed a specific extraction efficiency to the organic pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, while the superparamagnetic property of the NPs facilitated the convenient separation of MNPs from the bulk water samples. The modified NPs were not soluble in water, regardless of the alkyl chain and anions, although they could be dispersed ultrasonically. However, they were soluble and stable in polar organic solvents (e.g., MeOH, EtOH, and CH2Cl2); indicating their solubility and stability depend on the solvent. In strong polar solvents like MeOH and EtOH, the modified NPs with chloride as the anion were more soluble than those with PF6− as the anion. The solubility decreased with increasing alkyl chain length: hexyl > octyl > decyl. On the other hand, in CH2Cl2, a weak polar solvent, the modified NPs with PF6− as the anion were more soluble, with the solubility increasing with the increasing chain length: decyl > octyl > hexyl. Strangely, NP-OTIMPF6 (1-octyl-3-TIM hexafluorophosphate) had the highest solubility in both strong and weak polar solvents (Fig. 9). Neither naked NP nor modified NPs were soluble in nonpolar organic solvents, such as hexane.
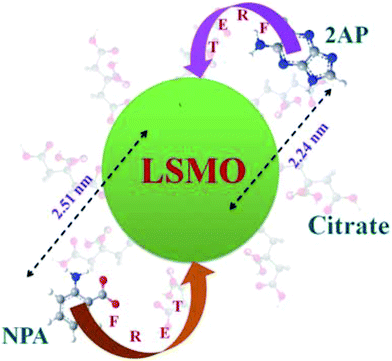
Certain attention is being paid to citrates88 and the mechanisms for their interactions with MNPs. Thus, molecular functionalization of the promising manganite nanoparticles La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 (LSMO) in citrate media for their solubilization in aqueous environments was studied.89 It was revealed that citrates are covalently attached to the surface of the NPs (Fig. 10). The calculated donor–acceptor distance is 2.24 nm, which indicates a very high efficiency of energy transfer and clearly supports the idea that 2AP was in close proximity to the solubilized LSMO NP surface. The prepared LSMO nanoparticles were rendered water-soluble using the reactivity of the carboxylate group of the citrate with the Mn center in LSMO, by two hours of extensive mixing using the cyclo-mixer. These functionalized manganite NPs could find application in the field of nanobiotechnology, as the solubilizing layer (citrate) provides multiple functional groups (hydroxyl and carboxylic acids) for covalent conjugation with other biological macromolecules, such as small peptides, DNA, RNA, and biocompatible polymers. In a related report,90 large-scale hydrophilic superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fig. 11; 20–40 nm in size) were prepared in the presence of citrate and sodium nitrate from ferrous ion alone. The Fe3O4 NPs were found to be quite stable and could be freely dispersed in water; the 20 nm particles had the best stability in water. A possible formation mechanism was proposed by the authors to explain why the magnetic nanoparticles are highly soluble in water; whereby, since the NPs are soluble in water but cannot be dissolved in alcohol, the charge of the citrate ions as surfactant must play a key role. The authors' proposal suggests that since there are three carboxyl groups in every citrate ion, the repulsive forces between the electric charges of the radical ions make the NPs more dispersed in water. At the same time, when the mass of NaNO3 is added into the reactive solution, the ionic strength is highly increased. This increase of ionic strength makes the charges of the NPs surrounding the citric acid radical become equally distributed. The presence of a large amount of salt thus changes the solubility of organic molecules. The presence of anions with a bigger hydrated ion radius will steady the water–oil interface and thus increase the solubility between the water and surfactant. It was also concluded that in the synthesis with ferrous ions alone (Reactions (1)–(3)), Fe3O4 is formed as a result of the dehydration reaction of ferrous hydroxide and ferric hydroxide, in which the latter compound is produced by the partial oxidation of ferrous hydroxide by O2 dissolved in water. The formation of Fe(OH)2 would be the first process in the synthesis. The transition temperature of Fe(OH)2 to Fe3O4 was found to be 60 °C.
| Fe2+ + 2OH− = Fe(OH)2 | (1) |
| 3Fe(OH)2 + ½O2 = Fe(OH)2 + 2FeOOH + H2O | (2) |
| Fe(OH)2 + 2FeOOH = Fe3O4 + 2H2O | (3) |
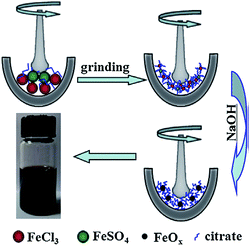
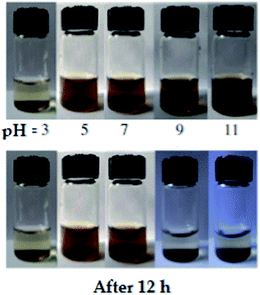
It was also found that the concentration of the Fe2+ ions is a key factor for controlling Fe3O4 NPs' sizes. A decrease of the ferrous precursor concentration from 0.1 M to 0.02 M allows an increase in the average size from 20 nm to 40 nm; a mean diameter of NPs of about 20 nm were prepared by using 0.10 M Fe2+ solution. If the concentration of the Fe2+ ions decreased to 0.05 M and 0.02 M, 25 nm and 40 nm Fe3O4 NPs could be obtained. In addition, citrates can be used for the functionalization of MNPs without any solvent for further solubilization. Thus, amorphous citrate-coated iron oxide nanoparticles with excellent water solubility were synthesized from FeCl3·2H2O and FeSO4·7H2O as the precursors at room temperature without the presence of any solvents (Fig. 12).91 The advantages of this method are based not only on its simplicity and nontoxicity, but also on its low cost, making it highly suitable for further applications. The authors proposed that the citrate formed a complex compound with Fe atoms in the first stage, which then facilitated the binding of carboxylate groups to the surface of iron oxide NPs in the second step. The citrate in this reaction plays a dual role as a complexing agent and as a stabilizer to prevent interparticle aggregation. The unique hydrophilic surface structure of the particles leads to the particles being stable in aqueous solution with different pH values from 5 to 7 (Fig. 13).
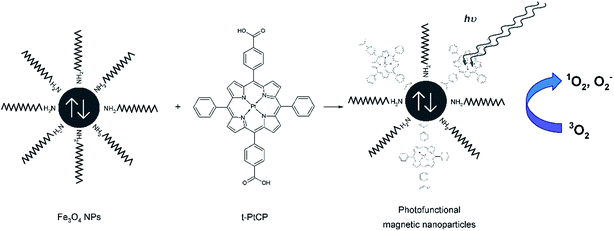
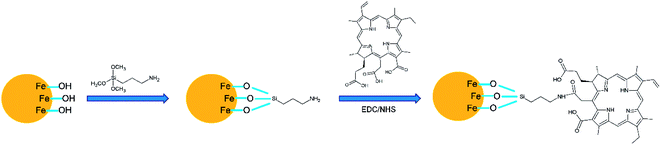
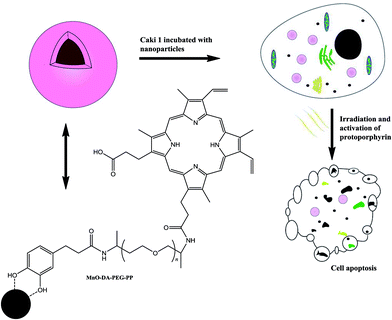
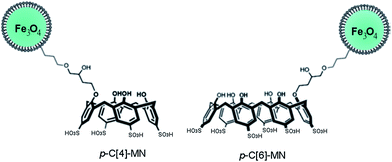
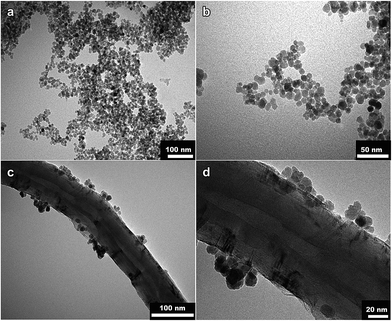
Derivatives of porphyrin-type macrocycles have also been observed as functionalizing units for MNP dissolution. Thus, a photofunctional magnetic nanoparticle, where the photofunctionality was provided by the photosensitizer (PS) of [5,15-bis(phenyl)-10,20-bis(4-methoxycarbonylphenyl)-porphyrin]-platinum (Fig. 14), thus generating singlet oxygen in high quantum yield, was strategically designed and prepared by a modification process.92 Fe3O4 nanoparticles covered with oleylamine, prepared from Fe(acac)3, 1,2-hexadecanediol, oleylamine, and phenyl ether, were used as precursors. It was shown that the immobilized PS molecules retain their optical and functional properties, including the high efficiency for singlet oxygen generation. The photofunctional magnetic nanoparticles have good solubility and stability in water, induced by the surface modification process. In a related report,93 PS-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles of ∼20 nm in diameter were strategically designed (Fig. 15) and prepared for gastric cancer imaging and therapy. The second generation PS chlorin e6 (Ce6) was covalently anchored onto the surface of magnetic nanoparticles with a silane coupling agent. The prepared Ce6-MNPs had high water solubility, non-cytotoxicity, good biocompatibility, and a remarkable photodynamic efficacy upon irradiation. Compared with MNPs-NH2, the zeta potentials of Ce6-MNPs all bear a negative charge (−23.72, −27.09, −24.94, −23.92, −21.91), which may be responsible for the prepared Ce6-MNPs' high water dispersibility and solubility. Finally, highly soluble superparamagnetic manganese oxide nanoparticles (Fig. 16) were synthesized by the thermal decomposition of manganese(II) oleate in 1-octadecene at elevated temperatures and then functionalized using a hydrophilic ligand containing protoporphyrin IX as PS (Fig. 17).94 The optical properties of protoporphyrin IX were found to be not significantly changed by binding to the MnO surface. These hydrophilic functionalized MnO nanoparticles showed the potential for application not only as imaging agents for MRI and fluorescence microscopy but also as target systems for photodynamic therapy. In addition to porphyrins, we note that calixarenes, for example, water-soluble calix[4,6]arene appended magnetic nanoparticles (p-C[4]-MN and p-C[6]-MN, Fig. 18), have been used for the removal of some carcinogenic aromatic amines.95 It was shown that sulfonic acid groups play a major role in the formation of hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions, similar to the Tiron-functionalized MNPs observed above.
Among all the functionalizing compounds, a variety of water-soluble polymers predominate in the experiments to solubilize MNPs; of which, we will show only the most representative examples. For instance, highly monodispersed magnetite NPs were prepared in organic solvents and subsequently transferred to water using a biocompatible amphiphilic polymer, in order to prepare them for use as suitable materials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia.96 {It is known97 that, in the above method, the heat dissipated from the superparamagnetic nanoparticles, in an alternating magnetic field can be used to locally raise the temperature by 5 °C or more above the physiological temperature (37 °C) in targeted tumor tissues, thereby encouraging either cell damage or death.} Indomethacin-loaded bilayer-surface magnetite nanoparticles (9 nm in size) are also described.98 These particles were first stabilized with oleic acid as a primary surfactant, followed by a poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-poly(3-caprolactone) (mPEG-PCL) amphiphilic block copolymer as a secondary surfactant, to form nanoparticles with a hydrophobic inner shell and hydrophilic corona. Studies on the transfer efficiency of the particles from hexane to the water phase showed that dispersibility of the particles in water was promoted by increasing the mPEG block lengths. This enables the possible tuning of their dispersibility in water by adjusting the ratio of the hydrophilic to hydrophobic moieties in the copolymer composition. The percentage of magnetite transferred to the water phase ranged from 78.9% to 91.2%, with the standard deviation ranging from 1.0% to 1.5%. The particles were stable in water, but with some aggregation observed after a one month period.
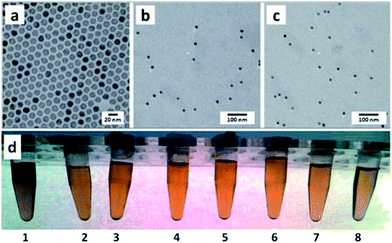
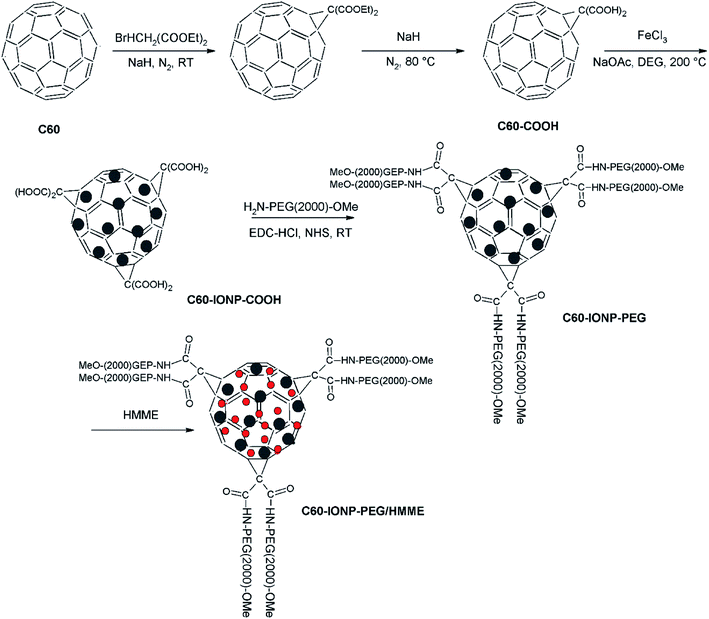
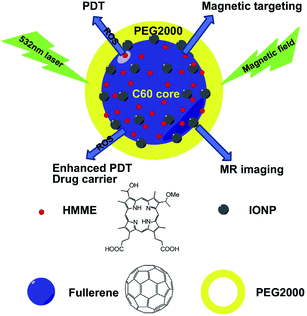
In addition to the example of the PEG-containing polymers above, iron oxide nanoparticles were also decorated onto the surface of fullerene (C60), and then a PEGylation was performed to improve the solubility and biocompatibility of C60-IONP, leading to a multifunctional C60-IONP-PEG nanocomposite with strong superparamagnetism and a powerful photodynamic therapy capacity (Fig. 19).99 The resulting C60-IONP-PEG exhibited excellent stability in water (Fig. 20) and in various physiological solutions, including saline, cell medium, and serum. Then, hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether (HMME), a new photodynamic anti-cancer drug, was conjugated to C60-IONP-PEG, forming a C60-IONP-PEG/HMME drug delivery system (Fig. 21). In in vitro and in vivo studies, C60-IONP-PEG/HMME showed excellent PDT efficacy, magnetic targeting properties and MRI abilities, indicating the great potential of C60-IONP-PEG/HMME for cancer theranostic applications.
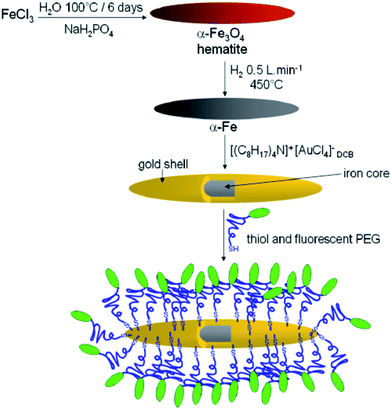
The gold surface of the Fe@Au NPs was functionalized (Fig. 22) with stained PEG thiol conjugates that enabled dispersion of the Fe@Au NPs into aqueous media.100 By using a redox transmetalation process, the Fe core served as a nanoelectrode for the spontaneous deposition of gold onto the surface of NPs, without the need for any additional agent. 70% (w/w) of particles were found to be magnetic, and the thickness of the gold layer was about 1.8 nm. In addition, water-soluble cobalt ferrite and manganese ferrite were used as model nanocrystals to illustrate the flexibility of sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation, since they are representative examples of two bimetallic ferrites with biomedical applications.101 This method is a cost-effective and easily scalable preparative technique that allows the sensitive evaluation and isolation of homogeneous, water-soluble nanoparticles. In particular, cobalt ferrite nanocrystals with a mean diameter of 6.0 nm were coated with 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG-2000) by hydrating a dry film containing a mixture of nanocrystals stabilized by oleic acid and DSPE-PEG-2000 (Fig. 23).
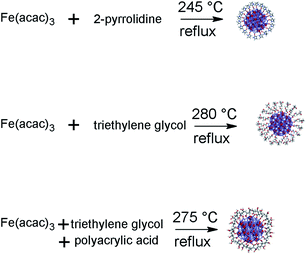
Three kinds of water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles (20–30 nm in size) capped with different surface functional groups, such as 2-pyrrolidone, triethylene glycol (TREG, see also the section on the “polyol strategy” below), and polyacrylic acid, were synthesized by the thermal decomposition method from Fe(acac)3 (Fig. 24).102 To investigate and improve the hydrophilicity of nanoparticles, polyacrylic acid (PAA, third route) was selected by the authors for functionalization of the magnetic nanoparticle surface, because of the copious amount of carboxylate groups along the polymer chain. These functional groups may enhance the interaction between water and the magnetic nanoparticles, because the free carboxylate groups extended in water may facilitate the dispersibility of polyacrylic acid magnetic nanoparticles in the aqueous solution. All three kinds of magnetic nanoparticles exhibited very hydrophilic properties and can be stably dissolved in water, even after being stored for three months. Their application as novel draw solutes in forward osmosis was investigated. Magnetic nanoparticles capped with polyacrylic acid can yield the highest driving force and subsequently highest water flux among the others. The used magnetic nanoparticles can be captured by a magnetic field and recycled back into the stream as draw solutes in the forward osmosis (FO) process.
Hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymers (HMWSPs) {comprised of a poly(sodium methacrylate) (PMANa) or poly(sodium acrylate) (PANa) backbone and pendent dodecyl methacrylate (DMA) or dodecyl acrylamide (DAAm) chains, respectively} were synthesized, and the hydrophobic CoFe2O4@OAm {oleylamine coated, solvothermally prepared from Fe(acac)3 and Co(acac)3 as precursors} MNPs were encapsulated into the hydrophobic cores of the structures formed by the copolymers above CMC (critical micelle concentration) through a solvent mixing procedure, resulting in hydrophilic CoFe2O4@HMWSP nanohybrids (Fig. 25).103 Two alternate phase transfer approaches were also used to convert CoFe2O4@OAm MNPs to hydrophilic ones: (a) the addition of a coating layer by cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB), and (b) by the ligand exchange procedure with 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA). Aqueous CoFe2O4@HMWSP, CoFe2O4@CTAB, and CoFe2O4@DMSA dispersions were prepared, and compared in terms of their stability. Related applications of polymethacrylic acid (PMAA)104 and PAA105 to obtain water-soluble NPs of iron oxides are also known.
Among the other uses of polymers for MNPs solubilization, a one-step, template-free synthesis method (Fig. 26) for preparing superparamagnetic polymeric microcapsules with iron oxide (γ-Fe2O3) magnetic nanoparticles embedded in the polymer shell (Fig. 27) was reported.106 Using an emulsification of the multiphase mixture containing liquid prepolymer (UV curable liquid photopolymer NOA 61) and nanoparticles in chloroform solution, double emulsions comprising a chloroform core and MPs/polymer shell were spontaneously formed. On exposure to UV light, these double emulsions were converted to microcapsules with a polymerized composite shell and could be moved and collected by external magnetic fields. One interesting property of these hybrid microcapsules is their ability to reversibly exchange water with the environment. When the emulsions were exposed to water by dilution of the glycerin medium, their cores readily swelled, due to the diffusion of water into the capsule interior. The authors believe that this core swelling is of osmotic origin and is due to the presence of a small amount of glycerin in the core. Moreover, when the shrunken dried capsules were redispersed in water after the chloroform in the core had completely evaporated, they reswelled to their initial spherical shape. Up to seven drying/watering cycles were repeated, and the capsules showed fully reversible shape restoration.
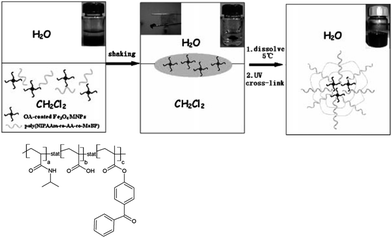
As a rare example of the special studies into the transformation of initially insoluble MNPs to soluble ones, we noted a facile and highly efficient method, described for transferring hydrophobic magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles from an organic to aqueous solution by wrapping a thermo-responsive and photo-crosslinkable poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAm) terpolymer encapsulating the particles (Fig. 28 and 29).107 The wrapping procedure was introduced by the co-nonsolvent transition of PNIPAm in the mixing solvent, so that the polymer could dissolve in water carrying Fe3O4 nanoparticles by noncovalent interactions. A related organic system was used to obtain a magnetically responsive microgel (Fig. 30), consisting of small IONPs (∼15 nm in diameter) embedded in a biocompatible microgel varying from ∼65 nm to ∼110 nm in diameter, which was obtained from FeCl3·6H2O and FeCl2·4H2O as precursors.108 Polymeric microgels were prepared by the emulsion-free copolymerization of thermoresponsive N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid with a water-soluble persulfate initiator.
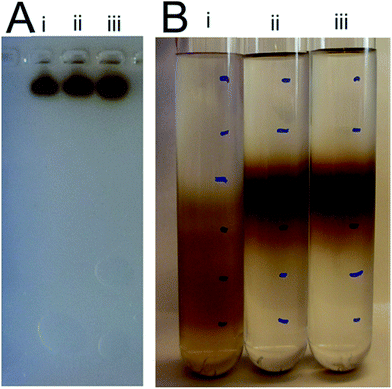
Also, superparamagnetic nanoparticles (magnetite Fe3O4) with a 5 nm diameter and stabilized in water (pH > 6.5) by a shell of water-soluble poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) chains were reported.109 Two types of diblock copolymers, i.e., poly(acrylic acid)-b-poly(ethylene oxide), PAA-PEO, and poly(acrylic acid)-b-poly(acrylate methoxy poly(ethyleneoxide)), PAA-PAMPEO, were prepared as stabilizers with different compositions and molecular weights. On the basis of the synthesized nanoparticles, the ferrofluids could be a source of heat when subjected to an alternating magnetic field. In addition, an efficient MRI T2-weighted contrast agent incorporating potential liver targeting functionality was synthesized via the combination of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles with multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs).110 Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) was coated onto the surface of acid-treated MWCNTs via electrostatic interactions, and SPIO nanoparticles modified with a potential targeting agent, lactose-glycine adduct (Lac-Gly), were subsequently immobilized onto the surface of the PDDA-MWCNTs (Fig. 31). Dispersion tests were conducted to determine the water dispersion stability of the product (CNT-PDDA-SPIO@Lac-Gly) in comparison with the starting material (MWCNTs) and the intermediate (CNT-PDDA). Pristine MWCNTs, CNT-PDDA, and CNT-PDDA-SPIO@Lac-Gly were initially dispersed in water with the assistance of ultrasonication for 30 min. As shown in Fig. 32, pristine MWCNTs could not be dispersed in water, even with assistance of ultrasound. However, CNT-PDDA and CNT-PDDA-SPIO@Lac-Gly could maintain a stable dispersion for more than 72 h, indicating that the PDDA coating improved the MWCNTs dispersions in aqueous solution. Fig. 33 shows TEM images of SPIO@Lac-Gly and CNT-PDDA-SPIO@Lac-Gly, respectively. Most of the SPIO@Lac-Gly particles had diameters of around 9 nm and were spherical in shape; the MWCNTs were covered with small clusters of magnetic nanoparticles, and no free nanoparticles were observed. The fabrication of water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles by ligand exchange with thermo-responsive polymers111 and chitosan112,113 is also known.
In additional to the compounds above for functionalization of MNPs, peptides can also be used for their solubilization. Thus, a method for the selective marking of amyloid fibrils, e.g., insulin and Aβ40, by both fluorescent and non-fluorescent γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles (15 nm in size) was developed.114 These IONPs of narrow size distribution were synthesized by nucleation, followed by the controlled growth of maghemite thin films onto gelatin–iron oxide nuclei, with further surface coatings with a functional fluorinated polymer and peptides, e.g., Leu-Pro-Phe-Phe-Asp (LPFFD) and Aβ40, through various activation methods. The authors note that, in contrast to many fluorescent nanoparticles that have their fluorescent moieties bound to the surface, their nanoparticles contained fluorescent dye, covalently encapsulated within the nanoparticles. This indicates a retention of the surface properties, including the zeta potential and the surface bound ligand capacity.
Coprecipitation
Coprecipitation generally consists in the simultaneous reduction of Fe2+/Fe3+ or Fen+/Au+ precursors, and it is frequently the first step before the functionalization of formed “naked” nanoparticles with organic moieties, as described above. Several surfactant coating and/or stabilizing agents could be added to the reaction system and the temperature may also vary. As an example, magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by coprecipitating a Fe2+/Fe3+ mixed solution (molar ratio of Fe2+![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Fe3+ = 1
Fe3+ = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2) with a NH4OH solution in air and mixed with oleic acid for coating with a single surfactant layer for further dispersion into methylene chloride.115 Water-soluble and biocompatible monodispersed ultrasmall magnetic iron nanoparticles (3.3 nm in diameter) were synthesized (Fig. 34) from FeCl3·6H2O and FeSO4·7H2O as precursors via a high-temperature coprecipitation method using thiol-functionalized poly(methacrylic acid) as the stabilizer.116 In addition, SPION with a mean size of 12 nm were prepared under N2 atmosphere, with the support of natural polymeric starch, by controlling chemical coprecipitation of the magnetite phase from aqueous solutions containing suitable salt ratios of Fe2+ and Fe3+.117 The surfaces of the SPION-nanoparticles were treated with a coordinatable agent (starch, dextran, PEG, or MPEG) for a higher dispersion ability in water and to retain the superparamagnetic behavior.
2) with a NH4OH solution in air and mixed with oleic acid for coating with a single surfactant layer for further dispersion into methylene chloride.115 Water-soluble and biocompatible monodispersed ultrasmall magnetic iron nanoparticles (3.3 nm in diameter) were synthesized (Fig. 34) from FeCl3·6H2O and FeSO4·7H2O as precursors via a high-temperature coprecipitation method using thiol-functionalized poly(methacrylic acid) as the stabilizer.116 In addition, SPION with a mean size of 12 nm were prepared under N2 atmosphere, with the support of natural polymeric starch, by controlling chemical coprecipitation of the magnetite phase from aqueous solutions containing suitable salt ratios of Fe2+ and Fe3+.117 The surfaces of the SPION-nanoparticles were treated with a coordinatable agent (starch, dextran, PEG, or MPEG) for a higher dispersion ability in water and to retain the superparamagnetic behavior.
Use of surfactants and capping agents
Surfactants are classical agents in nanotechnology and are widely used to prevent nanoparticle aggregation. As an example, nanoparticles of Fe, Co, FeCo, SmCo, and NdFeB systems with sizes smaller than 30 nm and a narrow size distribution were prepared by ball milling in the presence of surfactants (oleic acid and oleylamine, as mentioned in the sections above and in Table 1 below) and an organic carrier liquid.118 The nanoparticles prepared by milling Fe and FeCo powders were observed to be close to spherical in shape, whereas those of Co, SmCo, and Nd-Fe-B showed elongated rod shapes. The nanoparticles showed superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature, except for SmCo nanoparticles, which were ferromagnetic. When a surfactant was used along with heptane during the milling, a colored liquid (for nanoparticles smaller than 30 nm) was obtained, along with coarse particles, which sedimented at the bottom of the milling vial; when surfactants were not added to heptane, the solvent remained clear after milling, because there were no nanoparticles dispersed in the liquid.| Nanoparticles, size (nm) | Solvent(s) during the synthesis | Coating/capping or functionalizing agent/surfactant | NPS solubles in | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au- and Ag-coated Fe3O4, 12 nm | Chloroform | Au or/and Ag, oleylamine and oleic acid | Nonpolar solvents | 88 |
| Further treatment with CTAB and sodium citrate | Water | |||
| Fe3O4, 20–40 nm | Water | Sodium citrate | Water | 90 |
| Fe3O4, 30 nm | Benzyl ether | Oleylamine | Hexane and toluene | 80 |
| Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3, CoFe2O4, 6–15 nm; CoO, 50 nm | 1-Octadecene | Sodium oleate | Water | 78 and 96 |
| Fe3O4, 9 nm | Benzyl ether, further redispersion in hexane | Oleylamine and oleic acid; PEG diacid | Water or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) | 120 |
| Fe3O4, 9 nm | Benzyl ether | Oleylamine; mono-methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) (mPEG) | Both hexane and PBS | 82 |
| Fe3O4, 20 nm | Ethylene glycol (EG), diethylene glycol (DEG), triethylene glycol (TREG) and tetraethylene glycol (TEG) | EG, DEG, TREG or TEG | Water | |
| Fe3O4, 9 nm | MPEG | MPEG (used as a solvent, reducing agent, and modifying agent) | Water | 125 |
| Fe3O4, 5 nm | 1,2-Hexadecanediol and phenyl ether; further redispersion in hexane | Oleylamine; [5,15-bis(phenyl)-10,20-bis(4-methoxy-carbonyl-phenyl)-porphyrin] platinum (t-PtCP) | Water | 92 |
| γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4 | Water | Dextran, sucrose | Water | 119 |
| Fe3O4, 20 nm | 2-Pyrrolidone, triethylene glycol, and polyacrylic acid | 2-Pyrrolidone, triethylene glycol, and polyacrylic acid (PAA) | Water | 102 |
| Fe3O4, 5 nm | Toluene | Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) | Water | 109 |
| CoFe2O4, 5–7 nm | Diethylene glycol | Diethylene glycol | Diethylene glycol | 123 |
| CoFe2O4, 6 nm | — | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-ethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG-2000) | Water | 101 |
| MnO, 14 nm | 1-Octadecene; then chloroform and a solution of 30 mg DA-PEG-NH2 (3,4-dihydroxy-hydro-cinnamic acid) or DA-PEG-PP (dopamine-PEG-protoporphyrin IX) | Manganese(II) oleate (precursor) | Water | 94 |
Table 1 presents the most representative examples of classic magnetic nanoparticles, mainly soluble in water, as well as in some nonpolar organic solvents, and some examples of the solvents, surfactants, and capping agents applied for the synthesis and solubilization of magnetic nanoparticles. Here, we observe that nanoparticle synthesis, leading to dispersions, could be carried out both in water and in organic solvents. The use of sodium citrate and polyols generally leads to water-soluble polymers, while very frequent applications of oleylamine and oleic acid could assist the solubility in solvents of a specific nature. 1-Octadecene, polyols, and especially water are the most used solvents; sometimes the same compound acts as the solvent, surfactant, capping agent, and/or reductant (PAA or polyols). Water (“greener” solvent) possesses obvious advantages compared to organic solvents and so it is most frequently used.
Polyol strategy
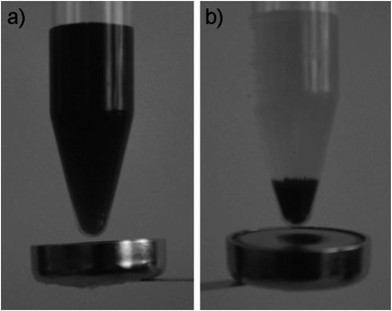
The polyol process is a versatile chemical approach, which refers to the use of polyols {for example, ethylene glycol (EG), diethylene glycol (DEG), triethylene glycol (TREG), and tetraethylene glycol (TEG)} to reduce metal salts to metal particles, and that has successfully been used to prepare a great variety of non-aggregated particles of inorganic compounds. Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG, an amphiphilic polymer and commonly regarded as a non-specific interaction reducing reagent), already mentioned in the sections above, is frequently used for the functionalization of MNPs.120 The polyols in this method often serve as a high-boiling solvent and reducing agent, as well as a stabilizer to control particle growth and prevent interparticle aggregating. In addition, PEG is an important biocompatible polymer that facilitates the solubilization and long-term circulation of proteins, viruses, and other biological macromolecules. Thus, magnetite nanoparticles (Fig. 35) were synthesized in liquid polyols at elevated temperatures.121 Polyol solvent was found to play a crucial role in determining the morphology and colloidal stability of the resulting particles. The magnetite nanoparticles were found to be monodisperse, highly crystalline, and superparamagnetic at r.t., and could be easily dispersed in aqueous media and other polar solvents, due to being coated by a layer of hydrophilic polyol ligands in situ. A distinguishing property of the magnetite nanoparticles obtained by the current synthesis approach from others obtained from a non-aqueous route is that the resulting magnetite nanoparticles exhibit excellent water solubility and no detectable aggregation is found. It is well known that magnetic colloidal particles attract each other by van der Waals forces and magnetic dipolar interactions. The authors hypothesize that the reason the as-prepared magnetite nanoparticles can be easily dissolved in high quantities in water to afford a stable aqueous solution is due to the formation of a steric barrier, which arises from the strong hydrophilic TREG ligands coated on the particles during the synthesis procedure. In addition, only a single iron rich precursor was used, and no further reducing agent or surfactants were required, which makes this process easy to scale-up for mass production. Also, the size distribution of the nanoparticles is much narrower than the particles produced from traditional methods. Magnetite nanoparticles obtained from Fe(acac)3 in TREG remained stable for several months, without noticeable precipitation.122The synthesis of spinel-type cobalt ferrite nanoparticles dispersed in diethylene glycol (DEG) was carried out via the polyol-mediated technique (Reaction (4)). The crystal size control could be achieved through successive synthesis steps;123 whereby, the technique was repeated in subsequent steps, using ferrite particles each time as seed, to finely tune the average size of the particles in the 5–7 nm range. The final concentrations of cobalt ferrite in stable dispersions for the specially prepared samples were found to be in the range of 0.15–2.88%. In addition, an interesting find observed in the case of iron oxide in PEG-containing systems, was that the high binding affinity of poly(ethylene glycol)-gallol (PEG-gallol) allows the freeze-drying and re-dispersion of 92 nm iron oxide cores individually stabilized with 9 nm-thick stealth coatings, affording particle stability for at least 20 months.124 Fig. 36 shows the prevention of particle agglomeration even in the presence of a small external magnet, when the surfactant is used. In all other interactions of “suspended MNPs – magnet”, observed in other reports, MNPs were attracted by magnets.
 | (4) |
Thermal decomposition
The thermal decomposition of the low stability precursors of MNPs (generally acetylacetonates or other iron coordination or organometallic compounds) can be carried out with or without the use of solvents. If the solvent is chosen appropriately, no other agents might be needed to obtain soluble MNPs. Thus, water-soluble superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with an average diameter of 9.5 ± 1.7 nm were synthesized by the thermal decomposition of Fe(acac)3 in MPEG (Fig. 37; methoxy polyethylene glycol, which was used as a solvent, reducing agent, and modifying agent in the shown reaction, and no further reducing agent or surfactants were required)125 or in TREG (triethylene glycol).126 MPEG molecules were shown to be covalently bound to the surface of the magnetite nanoparticles via the partial oxidation of the terminal OH group of the MPEG.Microwave heating
The reaction system treatment with microwaves (MW) is nowadays a classic tool in material chemistry and also in nanotechnology, and offers a number of advantages, as described elsewhere. In general, microwave synthesis has been shown to significantly reduce reaction time, increase yields, reduce side reactions, enhance reproducibility, and provide a more energy efficient, greener process. Microwave heating presents significant benefits over traditional heating methods (such as an oil bath), which rely on conduction and convection for heat distribution. Microwave radiation heats materials through the much more efficient dielectric heating, as molecular dipoles attempt to align with the alternating electric field. As an example of MW applications for the preparation of soluble MNPs, a rapid, straightforward microwave-assisted synthesis of superparamagnetic dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles was carried out.127 Two approaches were used: (1) uncoated iron oxide nanoparticles, basically iron cores with no coating, were prepared by the hydrazine reduction of ferric chloride with microwave heating at 100 °C for 10 minutes. A subsequent dextran coating of the nanoparticles was achieved in a second stage of microwave heating at 100 °C for 2 minutes. In the presence of additional ferric chloride, sodium hydroxide, and reduced dextran. (2) The nanoparticles were synthesized in a one-pot single step microwave reaction. Ferric chloride and reduced dextran were reacted with hydrazine in the microwave oven at 100 °C for 10 minutes. The two methods resulted in different sized nanoparticles. The dextran coating imparts the water solubility and biocompatibility necessary for in vivo utilization.Hydrothermal technique
A few reports have described the preparation of soluble Fe3O4 NPs in specific reaction systems. In one report, water-soluble Fe3O4 nanoparticles with a sufficiently high solubility (28 mg mL−1) and stability (at least one month) were synthesized through a hydrothermal approach using sodium citrate and ethylene diamine at 200 °C for 12 hours. It was found that they exhibited excellent removal ability for heavy-metal ions from wastewater.128 It is important that the adsorption ability of the water-soluble Fe3O4 NPs with Pb2+and Cr6+ is stronger than water-insoluble Fe3O4 NPs alone. In addition, the water-soluble Fe3O4 NPs exhibited relatively high saturation magnetization (83.4 emu g−1), which allowed their highly efficient magnetic separation from wastewater. Water-soluble magnetite used as an adsorbent could directly dissolve in water without the need for mechanical stirring or any extraneous forces. In a related report,129 water-soluble superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals, prepared through a hydrothermal approach (using Na2CO3 and ascorbic acid) at 160 °C for 3 h and capped with C6H6O6 (the oxidation state of ascorbic acid), could be readily dispersed in hydrated aqueous systems. The formation reactions (Reactions (5)–(7)) are as follows:| 2Fe3+ + 3CO32− + 6H2O → 2Fe(OH)3 + 3H2CO3 | (5) |
| 2Fe(OH)3 + C6H8O6 → 2Fe(OH)2 + C6H6O6 + 2H2O | (6) |
| 2Fe(OH)3 + Fe(OH)2 → Fe3O4 + 2H2O | (7) |
It was revealed that ascorbic acid not only serves as a reducing reagent for the reaction, but also the oxidation state of ascorbic acid takes part in surface coordination, which renders the magnetite nanocrystals water soluble and the colloidal solution stable. At the same time, these nanocrystals are difficult to be dispersed in ethanol. In the rinsing process, the products were washed by water, but the nanoparticles could not be separated from the solution by centrifugation. Therefore, the same volume of ethanol was introduced to this solution, and the magnetic particles were separated either by centrifugation or magnetic separation.
Stabilization of magnetic particles
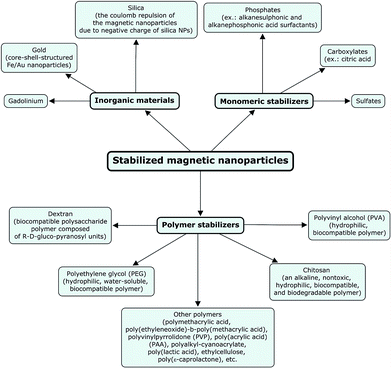
MNPs, transferred to water or organic solvents, or synthesized directly in situ, could be present in these phases during very different periods, depending on a series of factors, namely, particle size, surfactant/coating/functionalizing agent, temperature, etc. In terms of practical uses, the aggregation and sedimentation of magnetic nanoparticles can significantly affect their mobility and reactivity, which can subsequently influence the interaction between them and environmental contaminants, for instance, among other applications. So, dispersing bare nanoparticles into a stable suspension within the nanoscale range is an important step for studying the interaction of NPs with contaminants (e.g., toxic metals). Common treatments, such as ultrasound, frequently cause a temporal dispersion, in the majority of cases, with further precipitation. Stabilization of the magnetic particles can be achieved by acting on one or both of the two repulsive forces: electrostatic and steric repulsion (Fig. 38).130 Controlling the strength of these forces is a key parameter to elaborate particles with good stability. Steric forces are difficult to predict and quantify; whereas, electrostatic repulsion can be followed through knowledge of the diffusion potential, which may be very close to the zeta potential, and the Debye–Huckel length, which mainly depends upon the ionic strength, and the pH of the solution. Fig. 39 shows the main types of stabilizers for magnetic particles. | ||
| Fig. 38 (a) Particles stabilized by the electrostatic repulsion. (b) Particles stabilized by steric repulsion. | ||
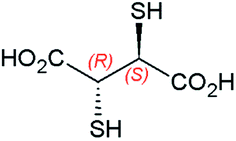
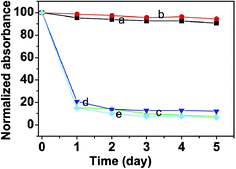
As a representative example for studying the stabilization of MNPs in aqueous media, hydrophilic 2,3-dimercaptosuccinnic acid {HOOC–CH(SH)–CH(SH)–COOH, DMSA, Fig. 40}-coated monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4) were dispersed in water, RPMI-1640 with 10% (v/v) fetal calf serum, RPMI-1640, PBS, and MES (4-morpholineethanesulfonic acid), respectively, to investigate their stability under biologically relevant conditions.131 It was elucidated that DMSA–Fe3O4 nanoparticles exist as aggregates under biological conditions. The stability of DMSA–Fe3O4 nanoparticles dispersed in water, RPMI-1640 with 10% (v/v) fetal calf serum, RPMI-1640, PBS, and MES, was also quantified (Fig. 41). Nanoparticles that are not stable and that sedimentate rapidly can be monitored by the decreased absorbance as a function of time. It was shown that DMSA–Fe3O4 nanoparticles dispersed in water and RPMI-1640 with fetal calf serum both present excellent stability, whereas those dispersed in RPMI-1640 without fetal calf serum, PBS, and MES exhibited poor stability, as demonstrated by a loss of less than 20% after five days for the former, whereas the latter lost more than 80%.
Special studies on MNPs solubilization and stability
Influence of precursors
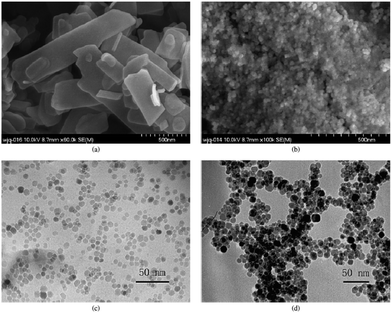
Pure magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4) were synthesized in water by coprecipitation using two different approaches, i.e., from: (a) ferrous sulfate, and (b) a mixture of ferrous and ferric chlorides.132 It was observed that the magnetite produced using ferrous sulfate could not be disaggregated, whereas magnetite produced from a mixture of ferrous and ferric chlorides could be disaggregated to a quasi-monodispersed form. The dispersing agents were tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide, Disperbyk 190, and polyacrylic acid (PAA). It was observed that the magnetic response of the washed, dispersed nanoparticles was significantly lower than that of the original material. The authors noted that type “a” reactions produced magnetite particles that were rhombic in shape, with sizes ranging from 30 nm to 150 nm diameter (Fig. 42a), when the reaction was stirred in excess OH−; whereas, material prepared under unstirred conditions and without excess OH− exhibited a nearly monodispersed, spherical morphology of 40 nm diameter. Nanoparticles produced using this method appeared to aggregate in an ordered fashion (chain, Fig. 42b). Whereas, type “b” reactions produced ultrasmall magnetite nanoparticles, with sizes ∼10 nm diameter (Fig. 42c). When TMAOH (tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide) was included in the synthesis (replacing NH4OH), the product consisted of quasispherical nanoparticles of ∼10 nm diameter (Fig. 42d). This material did not appear to aggregate in the same fashion as that of type (a) reaction products.Simulation of the state of dispersion
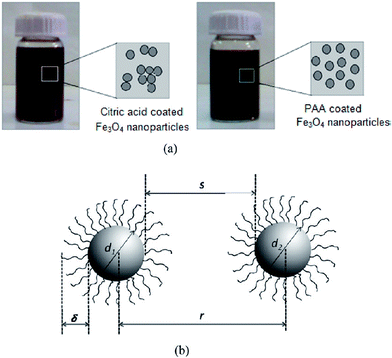
Monte Carlo simulation results predicting the state of dispersion (single, dimer, trimer, and so on) of citric-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles in an aqueous medium were compared with same the experimental data.133 The simulation was performed by calculating the total interaction potential between two nanoparticles as a function of their interparticle distance (Fig. 43) and applying a criterion for the two particles to aggregate, with the criterion being that the minimum depth of the secondary minima in the total interaction potential must be at least equal to kBT. The experiments showed that the citric acid-coated particles were mostly in the form of aggregates, whereas PAA-coated particles were isolated as individual particles. Both of these states of dispersion were predicted by the simulation. It was also observed that a minimum shell thickness was required for particles with a particular diameter, volume percentage, and grafting density in order for the dispersion to remain as isolated particles and in a stable state. For both the coating agents, suitable ranges of these experimentally controllable parameters, which can be experimentally realized to obtain a stable dispersion of individual isolated nanoparticles, were established.Additional ideas on the direct “hydrophobic → hydrophilic” transformation of MNPs
In general, there are three routes to modify hydrophobic NPs and render them soluble in aqueous biological buffers, as illustrated in Fig. 44.134 In the first approach, i.e., ligand exchange, the native monolayer of hydrophobic surface ligands is exchanged with ligands containing head groups that bind the magnetic NP surface and hydrophilic tails that interact with aqueous solvent. The ligand-exchange reaction is the major approach taken for the transformation of oil-soluble type functionalized IONPs into water-soluble type functionalized IONPs. The second approach involves an alternative solubilization strategy, in which the native hydrophobic ligands are retained on the magnetic nanoparticle surface through the adsorption of amphiphilic polymers onto the nanoparticle. These two general surface modification strategies present water-solubilizing groups, such as carboxyl acids and amines that are capable of covalent conjugation, with appropriate functional groups on the desired biomolecules. The third approach for magnetic NP surface modification is the fabrication of an inorganic shell, typically consisting of silica or gold, by one of two general schemes, namely by precipitation and reaction at the NP surface, or by the deposition of preformed colloids onto the NP surface. As a representative example of this third approach, magnetic nanoparticles, MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4, were stabilized by the deposition of an Al(OH)3 layer via a hydrolysis process.135 The particles displayed excellent colloidal stability in water and a high affinity to 18F-fluoride and bisphosphonate groups. The properties of the particles were found to be strongly dependent on the thickness and hardness of the Al(OH)3 layer, which could in turn be controlled by the hydrolysis method. In particular, the nanoparticulate MnFe2O4 was soluble in hexane, but insoluble in water, due to the organic layer (oleylamine and oleic acid) on the surface. Once coated with Al(OH)3, the NPs become soluble in water, but insoluble in hexane (Fig. 45). All of these features suggest that a coating of Al(OH)3 replaced the oleylamine on the iron oxide NPs. However, it is necessary to take into account that there were no obvious differences in size or morphology before and after the coating with Al(OH)3. | ||
| Fig. 45 Photographs of MnFe2O4 (left) and MnFe2O4@Al(OH)3 (right) NPs in a two-phase mixture of hexane (upper layer) and water (lower layer). | ||
Ultrasonic treatment
When one needs to disperse insoluble NPs, the first thought is normally to apply ultrasonic treatment. Ultrasonic techniques in chemistry and technology are now classic tools, and have been described elsewhere. Sometimes, several studies are carried out to compare its effectiveness with other techniques. Thus, different techniques to disperse bare IONPs (e.g., vortex, bath sonication, probe ultrasonication) and the effects of important environmental factors, such as dissolved organic matter and ionic strength in the stability of IONPs dispersions, were investigated.136 As a result, it was seen that the vortex minimally dispersed IONPs, with the hydrodynamic diameter being outside of the “nanosize range” (698–2400 nm). Similar to a vortex, bath sonication could also not disperse IONPs efficiently. Probe ultrasonication was found to be more effective at dispersing IONPs (50% or more), with hydrodynamic diameters ranging from 120 nm to 140 nm with minimal changes in size and sedimentation of IONPs for a prolonged period of time, although probe ultrasonication did not break the IONPs down into their primary particle size. In addition, although sedimentation occurred to some extent, a considerable amount of IONPs remained in suspension in the presence and absence of 100 mg L−1 HA (humic acid) and 0.1 mM NaCl. The authors showed that high ionic strengths increased the colloidal instability, by compressing the electrical double layer thickness, causing rapid aggregation and sedimentation. On the other hand, electrostatic repulsive forces dominated at low ionic strengths, resulting in reduced destabilization of the dispersions.Use of magnetic fields
We observed in different reports that magnetic fields can be applied both for the aggregation and deaggregation of nanoparticles in general. Thus, for non-magnetic nanoparticles (for example, silica or alumina), magnetohydrodynamic nanoparticle dispersion is an energy efficient method to deaggregate nanoparticles, combining hydrodynamic forces of turbulent flow with Lorentz forces generated by a magnetic field.137 On the other hand, for MNPs, nanoparticle aggregation influenced by magnetic fields was studied using FeO(OH).138 The nanoparticles were shown to exist not only in stable (pH 2) and flocculated (pH 6) states, but also in a metastable aggregated state at an intermediate pH between 3 and 5. Thus, colloidally stable nanoparticle suspensions of iron hydroxide FeO(OH) at pH 2 were prepared and shown to be non-magnetic. However, when the pH of the dispersion was raised to destabilize the suspension, aggregates near 200 nm diameter were detected, and these were influenced by magnetic fields in the 50 kA m−1 range. These aggregates were unusual in that they were colloidally stable and did not behave as flocs. The authors called them “nucleags” (Fig. 46) to distinguish them from conventional flocculated agglomerates. By increasing the pH, flocculation of the nanoparticles was observed and a brown sludge, which was not influenced by magnetic fields, was deposited on the base of the container. These metastable aggregates were influenced by small pH changes, showing that the adhesion between the nanoparticles was small. The concentration of these metastable aggregates was very low, typically 5 ppb at pH 3.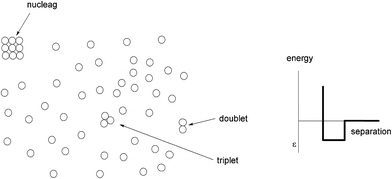 | ||
| Fig. 46 (a) Schematic of the dispersion containing metastable nuclei, defined as nucleags. (b) The square well interaction potential between nanoparticles. | ||
Conclusions and further outlooks
Magnetic nanoparticles (generally based on iron) could be solubilized in water (most frequently, due to their potential in medical applications) or non-aqueous solvents for short or long time periods. The main approaches needed to carry out this goal are the suitable choice of precursors, pH, surfactants/coating agents, and solvents, as well as functionalizing agents for the MNPs. Generally, MNPs can be solubilized by functionalization with water-soluble compounds/moieties (in particular soluble polymers, porphyrins, and calixarenes), under conditions of the thermal decomposition of low-stability metal complexes, coprecipitation, or more rarely by microwave heating or other high-temperature methods. The polyol strategy is frequently applied for increasing the solubility of MNPs. Stabilization of the MNPs could be achieved with the aid of inorganic, monomeric, and polymeric compounds. Regular functional groups in the surfactants and coating agents used for the dispersion of magnetic nanoparticles include –NH2 (oleylamine), –COOH, and –COO− {oleic acid, DMSA, sodium oleate, citrates, as well as the sodium salts of polymethacrylic and polyacrylic acids (PMANa and PANa)}, –OH {polyols (EG, DEG, TEG, TREG), Tiron, DA}, and the acetylacetonate anion. Other compounds include polymers (PNIPAm, PEO), small and larger macrocycles (calixarenes and porphyrin-type molecules), polysaccharides (dextran, sucrose), and biomolecules (peptides), among others.The synthesis of soluble nanoparticles can be carried out both in water and in organic solvents. The use of sodium citrate and polyols generally results in water-soluble polymers; while, the very frequent application of oleylamine and oleic acid could lead to solubility in solvents of a specific nature. 1-Octadecene, polyols, and especially water, are the most commonly used solvents. Sometimes the same compound acts as a solvent, surfactant, capping agent, and/or reductant (PAA or polyols). Water (a “greener” solvent) possesses obvious advantages compared to organic solvents, and hence, it is the mostly commonly used.
Currently, as seen above, not all experimental techniques currently used for the preparation of magnetic nanoparticles are suitable for the synthesis of soluble or dispersed MNPs. Taking into account the wide range of applications for solubilized MNPs,139–141 e.g., first of all in bio-nanomedicine and the treatment of contaminants in the environment, we believe that the number of solubilization and dispersion techniques applied for aqueous systems will increase considerably in the next 5–10 years.
References
- A. Akbarzadeh, M. Samiei and S. Davaran, Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2012, 7(144), 13 Search PubMed.
- H. Bin Na, I. Chan Song and T. Hyeon, Inorganic Nanoparticles for MRI Contrast Agents, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 2133–2148 CrossRef.
- V. V. Mody, A. Cox, S. Shah, A. Singh, W. Bevins and H. Parihar, Magnetic nanoparticle drug delivery systems for targeting tumor, Appl. Nanosci., 2014, 4(4), 385–392 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Pandey and M. H. Fulekar, Nanotechnology: remediation technologies to clean up the environmental pollutants, Res. J. Chem. Sci., 2012, 2(2), 90–96 CAS.
- S. P. Gubin, Magnetic Nanoparticles, Wiley, 2009, p. 483 Search PubMed.
- N. P. Sabbas, Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties and Role in Biomedicine, Series: Nanotechnology Science and Technology, Nova Science Publishers, Inc., 2014, p. 245 Search PubMed.
- Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications, ed. N. T. K. Thanh, CRC Press, 2012, p. 616 Search PubMed.
- X. Peng, H. Chen, J. Huang, H. Mao and D. M. Shin, Targeted Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging and Therapy, in Biomedical Engineering – From Theory to Applications, ed. Prof. Reza Fazel, INTECH, 2011, pp. 204–224 Search PubMed.
- S. Bucak, B. Yavuztürk and A. Demir Sezer, Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Surface Modifications and Application in Drug Delivery, in Recent Advances in Novel Drug Carrier Systems, InTech, 2012 Search PubMed.
- T. K. Indira and P. K. Lakshmi, Magnetic nanoparticles – a review, Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol., 2010, 3(3), 1035–1042 CAS.
- S. P. Gubin, Yu. A. Koksharov, G. B. Khomutov and G. Yu. Yurkov, Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, structure and properties, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2005, 74(6), 489–520 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Faraji, Y. Yamini and M. Rezaee, Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Functionalization, Characterization, and Applications, J. Iran. Chem. Soc., 2010, 7(1), 1–37 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mohapatra and S. Anand, Synthesis and applications of nano-structured iron oxides/hydroxides – a review, Int. J. Eng. Sci. Tech., 2010, 2(8), 127–146 Search PubMed.
- C. Blanco-Andujar, L. Duc Tung and N. T. K. Thanh, Synthesis of nanoparticles for biomedical applications, Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem., Sect. A: Inorg. Chem., 2010, 106, 553–568 RSC.
- A. H. Lu, E. L. Salabas and F. Schuth, Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 1222–1244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Fei, Z. Jing-Han, H. Yang-Long and G. Song, Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanocrystals: recent progress, Chin. Phys. B, 2013, 22(10), 107503 CrossRef.
- R. Hao, R. Xing, Z. Xu, Y. Hou, S. Gao and S. Sun, Synthesis, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications of Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 2729–2742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sheng-Nan, W. Chao, Z. Zan-Zan, H. Yang-Long, S. S. Venkatraman and X. Zhi-Chuan, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface coating techniques for biomedical applications, Chin. Phys. B, 2014, 23(3), 037503 CrossRef.
- H.-Y. Park, M. J. Schadt, L. Wang, I.-I. Stephanie Lim, P. N. Njoki, S. Hong Kim, M.-Y. Jang, J. Luo and C.-J. Zhong, Fabrication of Magnetic Core@Shell Fe Oxide@Au Nanoparticles for Interfacial Bioactivity and Bio-separation, Langmuir, 2007, 23, 9050–9056 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. M. Parkes, R. Hodgson, L. T. Lu, L. D. Tung, I. Robinson, D. G. Fernig and N. T. K. Thanh, Cobalt nanoparticles as a novel magnetic resonance contrast agent – relaxivities at 1.5 and 3 Tesla, Contrast Media Mol. Imaging, 2008, 3, 150–156 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Cojocariu, A. Doaga, W. Amin, P. Bender, R. Hempelmann and O. F. Caltun, Synthesis and functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with possible application in drug delivery, Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 2013, 8(2), 519–527 Search PubMed.
- P. Gould, Nanomagnetism shows in vivo potential, Nano Today, 2006, 1(4), 34–39 CrossRef.
- S. Mørup, M. Fougt Hansen and C. Frandsen, Magnetic interactions between nanoparticles, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol., 2010, 1, 182–190 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Kowalczyk, I. Lagzi and B. A. Grzybowski, Nanoseparations: strategies for size and/or shape-selective purification of nanoparticles, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 16, 135–148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. D. Moeser, K. A. Roach, W. H. Green, T. Alan Hatton and P. E. Laibinis, High-Gradient Magnetic Separation of Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles, AIChE J., 2004, 50(11), 2835–2848 CrossRef CAS.
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed (the “Gold Book”), Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1997, XML on-line corrected version: http://goldbook.iupac.org (2006-) created by M. Nic, J. Jirat, B. Kosata; updates compiled by A. Jenkins, ISBN 0-9678550-9-8, DOI:10.1351/goldbook.
- S. Slomkowski, J. V. Alemán, R. G. Gilbert, M. Hess, K. Horie, R. G. Jones, P. Kubisa, I. Meisel, W. Mormann, S. Penczek and R. F. T. Stepto, Terminology of polymers and polymerization processes in dispersed systems (IUPAC Recommendations 2011), Pure Appl. Chem., 2011, 83(12), 2229–2259 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Pomogailo and V. N. Kestelman, Metallopolymer Nanocomposites, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2005, pp. 65–66 Search PubMed.
- T. Premkumar, R. Mezzenga and K. E. Geckeler, Carbon nanotubes in the liquid phase: addressing the issue of dispersion, Small, 2012, 8(9), 1299–1313 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kraynov and T. E. Müller, Concepts for the Stabilization of Metal Nanoparticles in Ionic Liquids, in Applications of Ionic Liquids in Science and Technology, ed. Scott Handy, 2011 Search PubMed.
- N. A. Frey, S. Peng, K. Cheng and S. Sun, Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, functionalization, and applications in bioimaging and magnetic energy storage, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(9), 2532–2542 RSC.
- M. Mahdavi, M. Bin Ahmad, Md. Jelas Haron, F. Namvar, B. Nadi, M. Zaki Ab Rahman and J. Amin, Synthesis, Surface Modification and Characterisation of Biocompatible Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications, Molecules, 2013, 18, 7533–7548 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Qu, H. Ma, W. Zhou and C. J. O'Connor, In situ surface functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with hydrophilic natural amino acids, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2012, 389(1), 60–65 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Cheraghipour, S. Javadpour and A. Reza Mehdizadeh, Citrate capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles used for hyperthermia therapy, J. Biomed. Sci. Eng., 2012, 5, 715–719 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Jagminas, K. Mažeika, R. Kondrotas, M. Kurtinaitienė, A. Jagminienė and A. Mikalauskaitė, Functionalization of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles by a Vitamin C-assisted Covering with Gold, Nanomater. Nanotechnol., 2014, 4(11), 9 Search PubMed.
- A. S. S. Ibrahim, A. A. Al-Salamah, A. M. El-Toni, M. A. El-Tayeb and Y. B. Elbadawi, Immobilization of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase on aminopropyl-functionalized silica-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles, Electron. J. Biotechnol., 2013, 16(6), 1–16 CAS.
- R. A. Sperling and W. J. Parak, Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles, Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 2010, 368(1915), 1333–1383 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Arslan, T. N. Gevrek, J. Lyskawa, S. Szunerits, R. Boukherroub, R. Sanyal, P. Woisel and A. Sanyal, Bioinspired Anchorable Thiol-Reactive Polymers: Synthesis and Applications Toward Surface Functionalization of Magnetic Nanoparticles, Macromolecules, 2014, 47(15), 5124–5134 CrossRef CAS.
- K. M. Gregorio-Jauregui, M. Guadalupe Pineda, J. E. Rivera-Salinas, G. Hurtado, G. Saade, J. E. Martinez, A. Ilyina and R. G. López, One-Step Method for Preparation of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Chitosan, J. Nanomater., 2012, 2012, 813958 Search PubMed.
- Z.-C. Xing, Y. Chang and I.-K. Kang, Immobilization of biomolecules on thesurface of inorganic nanoparticles forbiomedical applications, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2010, 11, 014101 CrossRef , 17pp.
- K. Turcheniuk, A. V. Tarasevych, V. P. Kukhar, R. Boukherrouba and S. Szunerits, Recent advances in surface chemistry strategies for the fabrication of functional iron oxide based magnetic nanoparticles, Nanoscale, 2013, 5, 10729–10752 RSC.
- A. L. Andrade, D. M. Souza, M. C. Pereira, J. D. Fabris and R. Z. Domingues, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with silica through a sol–gel approach, Cerâmica, 2009, 55(336), 420–424 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Van Quy, N. M. Hieu, P. T. Tra, N. H. Nam, N. H. Hai, N. T. Son, P. T. Nghia, N. T. Van Anh, T. T. Hong and N. H. Luong, Synthesis of Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and Application in the Detection of Pathogenic Viruses, J. Nanomater., 2013, 2013, 603940 Search PubMed.
- G. V. Pavan Kumar, N. Rangarajan, B. Sonia, P. Deepika, N. Rohman and C. Narayana, Metal-coated magnetic nanoparticles for surface enhanced Raman scattering studies, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2011, 34(2), 207–216 CrossRef PubMed.
- Nanoparticles Synthesis, Stabillization, Passivation and Functionalization, ed. R. Nagarajan and T. Alan Hatton, ACS Symposium Series, 2008, Book 996, 464 pp Search PubMed.
- P. Loekitowati Hariani, M. Faizal, Ridwan, Marsi and D. Setiabudidaya, Synthesis and Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Co-precipitation Method to Removal Procion Dye, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev., 2013, 4(3), 336–340 CrossRef.
- U. Wiedwald, L. Han, J. Biskupek, U. Kaiser and P. Ziemann, Preparation and characterization of supported magnetic nanoparticles prepared by reverse micelles, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol., 2010, 1, 24–47 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. F. Hasany, I. Ahmed, J. Rajan and A. Rehman, Systematic Review of the Preparation Techniques of Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles, Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2012, 2(6), 148–158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Banerjee, S. Roy, J. W. Chen and D. Chakravorty, Magnetic properties of oxide-coated iron nanoparticles synthesized by electrodeposition, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2000, 219(1), 45–52 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bellusci, C. Aliotta, D. Fiorani, A. La Barbera, F. Padella, D. Peddis, M. Pilloni and D. Secci, Manganese iron oxide superparamagnetic powder by mechanochemical processing. Nanoparticles functionalization and dispersion in a nanofluid, J. Nanopart. Res., 2012, 14, 904 CrossRef.
- G. Saito, Y. Nakasugi, T. Yamashita and T. Akiyama, Solution plasma synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles, Nanotechnology, 2014, 25, 135603 CrossRef PubMed , 7pp.
- L. Zhang and Y. Wu, Sol–Gel Synthesized Magnetic Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles as Novel Catalyst for Oxidative Degradation of Methyl Orange, J. Nanomater., 2013, 2013, 640940 Search PubMed.
- S. Chaitoglou, M. Reza Sanaee, N. Aguiló-Aguayo and E. Bertran, Arc-Discharge Synthesis of Iron Encapsulated in Carbon Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications, J. Nanomater., 2014, 2014, 178524 Search PubMed.
- R. Strobel and S. E. Pratsinis, Direct synthesis of maghemite, magnetite and wustite nanoparticles by flame spray pyrolysis, Adv. Powder Technol., 2009, 20(2), 190–194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Martínez, A. Malumbres, R. Mallada, J. L. Hueso, S. Irusta, O. Bomatí-Miguel and J. Santamaría, Use of a polyol liquid collection medium to obtain ultrasmall magnetic nanoparticles by laser pyrolysis, Nanotechnology, 2012, 23(42), 425605 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Salazar-Alvarez, M. Muhammed and A. A. Zagorodni, Novel flow injection synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles with narrow size distribution, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2006, 61(14), 4625–4633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Soundararajan and K. Hyeon Kim, Synthesis of CoFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles by Thermal Decomposition, Journal of Magnetics, 2014, 19(1), 5–9 CrossRef.
- H. Zhang and G. Zhu, One-step hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles immobilized on polyamide fabric, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258(11), 4952–4959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Y. Haw, F. Mohamed, C. H. Chia, S. Radiman, S. Zakaria, N. M. Huang and H. N. Lim, Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents, Ceram. Int., 2010, 36, 1417–1422 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Chen, C. Li, Y.-J. Zhu, X.-Y. Zhao, B.-Q. Lub and J. Wu, Magnetic nanocomposite of hydroxyapatite ultrathin nanosheets/Fe3O4 nanoparticles: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis and application in pH-responsive drug release, Biomater. Sci., 2013, 1, 1074–1081 RSC.
- C. Li, Y. Wei, A. Liivat, Y. Zhu and Y. Zhua, Microwave-solvothermal synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, Mater. Lett., 2013, 107(15), 23–26 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. S. Martirosyan, C. Dannangoda, E. Galstyan and D. Litvinov, Screen-printing of ferrite magnetic nanoparticles produced by carbon combustion synthesis of oxides, J. Appl. Phys., 2012, 111, 094311 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Mosleh, P. Kamelin, M. Ranjbar and H. Salamati, Effect of annealing temperature on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles, Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, 7279–7284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bystrzejewski, M. Szala, W. Kicinski, W. Kaszuwara, M. H. Rummeli, T. Gemming and A. Huczko, Self-sustaining high-temperature synthesis of carbon-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles from organic and inorganic metal precursors, New Carbon Mater., 2010, 25(2), 81–88 CrossRef CAS.
- C.-X. Zhao, K. He, S. Z. Qiao and A. P. J. Middelberg, Nanoparticle synthesis in microreactors, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2011, 66, 1463–1479 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. T. Klem, M. Young and T. Douglas, Biomimetic magnetic nanoparticles, Mater. Today, 2005, 8(9), 28–37 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Yang and R. Dimova, Nanoparticle Synthesis in Vesicle Microreactors, in Biomimetic Based Applications, ed. A. George, InTech, 2011, pp. 523–553 Search PubMed.
- C. Okoli, M. Boutonnet, L. Mariey, S. Järås and G. Rajarao, Application of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles prepared from microemulsions for protein purification, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2011, 86(11), 1386–1393 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Karthikeyeni, T. Siva Vijayakumar, S. Vasanth, A. Ganesh, M. Manimegalai and P. Subramanian, Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and its haematological effects on fresh water fish Oreochromis mossambicus, J. Acad. Ind. Res., 2013, 1(10), 645–649 Search PubMed.
- M. Mahdavi, F. Namvar, M. Bin Ahmad and R. Mohamad, Green Biosynthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Sargassum muticum) Aqueous Extract, Molecules, 2013, 18, 5954–5964 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. Safarik and M. Safarikova, Magnetic nanoparticles and biosciences, Monatsh. Chem., 2002, 133, 737–759 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Wu, Q. He and C. Jiang, Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2008, 3, 397–415 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Rajnak, J. Tothova, J. Kovac, J. Kurimsky, B. Dolnik, P. Kopcansky, M. Molcan, F. Royer and M. Timko, Dynamical properties of transformer oil based magnetic fluids. Proceedings of the 7th 7 International Pamir Conference Fundamental and Applied MHD and COST P17 Annual Workshop 2008, Presqu'Ile de Giens, France, September 8–12, 2008, pp. 737–742 Search PubMed.
- P. Kopcansky, N. Tomasovicova, M. Koneracka, M. Timko, V. Zavisova and L. Tomco, Magnetic nanoparticles in magnetic fluids, Acta Electrotechnica et Informatica, 2010, 10(3), 10–13 Search PubMed.
- A. Z. Wilczewska, K. Niemirowicz, K. H. Markiewicz and H. Car, Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems, Pharmacol. Rep., 2012, 64, 1020–1037 CrossRef CAS.
- S. C. N. Tang and I. M. C. Lo, Magnetic nanoparticles: essential factors for sustainable environmental applications, Water Res., 2013, 47(8), 2613–2632 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hou, Z. Xu and S. Sun, Controlled Synthesis and Chemical Conversions of FeO Nanoparticles, Angew. Chem., 2007, 119, 6445–6448 CrossRef.
- Z. Xu, C. Shen, Y. Tian, X. Shi and H.-J. Gao, Organic phase synthesis of monodisperse iron oxide nanocrystals using iron chloride as precursor, Nanoscale, 2010, 2, 1027–1032 RSC.
- M. Klokkenburg, J. Hilhorst and B. H. Erne, Surface analysis of magnetite nanoparticles in cyclohexane solutions of oleic acid and oleylamine, Vib. Spectrosc., 2007, 43, 243–248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xu, C. Shen, Y. Hou, H. Gao and S. Sun, Oleylamine as Both Reducing Agent and Stabilizer in a Facile Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles, Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 1778–1780 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zeng, R. Hao, B. Xing, Y. Hou and Z. Zhichuan Xu, One-pot synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoprisms with controlled electrochemical properties, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 3920–3922 RSC.
- J. Xie, C. Xu, Z. Xu, Y. Hou, K. L. Young, S. X. Wang, N. Pourmand and S. Sun, Linking Hydrophilic Macromolecules to Monodisperse Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles via Trichloro-s-Triazine, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 5401–5403 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kus, F. Ozel, N. M. Varal and M. Ersoz, Luminescent enhancement of OLED performance by doping colloidal magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, Prog. Electromagn. Res., 2013, 134, 509–524 CrossRef.
- Z. Liang and X. Wu, A Facile Approach to Fabricate Water-soluble Au–Fe3O4 Nanoparticle for Liver Cancer Cells Imaging, Chin. J. Chem., 2012, 30, 1387–1392 CrossRef CAS.
- K. V. Korpany, F. Habib, M. Murugesu and A. Szuchmacher Blum, Stable water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles using Tiron, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2013, 138, 29–37 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. K. Nagesha, B. D. Plouffe, M. Phan, L. H. Lewis, S. Sridhar and S. K. Murthy, Functionalization-induced improvement in magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for biomedical applications, J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 105, 07B317 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Li, N. Tang, F. Inagaki, C. Mukai and K. Hayakawa, Characterization and Functionality of Immidazolium Ionic Liquids Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles, J. Chem., 2013, 7 Search PubMed Article ID 861021.
- Z. Xu, Y. Hou and S. Sun, Magnetic Core/Shell Fe3O4/Au and Fe3O4/Au/Ag Nanoparticles with Tunable Plasmonic Properties, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 8698–8699 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Giri, A. Makhal, B. Ghosh, A. K. Raychaudhuri and S. Kumar Pal, Functionalization of manganite nanoparticles and their interaction with biologically relevant small ligands: picosecond time-resolved FRET studies, Nanoscale, 2010, 2, 2704–2709 RSC.
- C. Hui, C. Shen, T. Yang, L. Bao, J. Tian, H. Ding, C. Li and H.-J. Gao, Large-Scale Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Soluble in Water Synthesized by a Facile Method, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 11336–11339 CAS.
- Z. Wang, L. Zhao, P. Yang, Z. Lv, H. Sun and Q. Jiang, Water-soluble amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by a quickly pestling and nontoxic method at room temperature as MRI contrast agents, Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 235, 231–235 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K.-H. Choi, K.-K. Wang, E. Pil Shin, S.-L. Oh, J.-S. Jung, H.-K. Kim and Y.-R. Kim, Water-Soluble Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized with Photosensitizer for Photocatalytic Application, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 3212–3219 CAS.
- P. Huang, Z. Li, J. Lin, D. Yang, G. Gao, C. Xu, L. Bao, C. Zhang, K. Wang, H. Song, H. Hu and D. Cui, Photosensitizer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for in vivo simultaneous magnetofluorescent imaging and targeting therapy, Biomaterials, 2011, 32(13), 3447–3458 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. D. Schladt, K. Schneider, M. I. Shukoor, F. Natalio, H. Bauer, M. Nawaz Tahir, S. Weber, L. M. Schreiber, H. C. Schroder, W. E. G. Muller and W. Tremel, Highly soluble multifunctional MnO nanoparticles for simultaneous optical and MRI imaging and cancer treatment using photodynamic therapy, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 8297–8304 RSC.
- T. Aksoy, S. Erdemir, H. B. Yildiz and M. Yilmaz, Novel Water-Soluble Calix[4,6]arene Appended Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Removal of the Carcinogenic Aromatic Amines, Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 2012, 223, 4129–4139 CrossRef CAS.
- A. P. Khandhar, R. Matthew Ferguson and K. M. Krishnan, Monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles optimized for magnetic fluid hyperthermia: implications in biological systems, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109, 07B310 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Lahonian, Diffusion of Magnetic Nanoparticles Within a Biological Tissue During Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia, in Hyperthermia, ed. N. Huilgol, INTECH, 2013 Search PubMed.
- M. Rutnakornpituk, S. Meerod, B. Boontha and U. Wichai, Magnetic core-bilayer shell nanoparticle: a novel vehicle for entrapment of poorly water-soluble drugs, Polymer, 2009, 50, 3508–3515 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Shi, X. Yu, L. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Gao, J. Zhang, R. Ma, R. Liu and Z. Zhang, PEGylated fullerene/iron oxide nanocomposites for photodynamic therapy, targeted drug delivery and MR imaging, Biomaterials, 2013, 34, 9666–9677 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Mendez-Garza, B. Wang, A. Madeira, C. Di Giorgio and G. Bossis, Synthesis and Surface Modification of Spindle-Type Magnetic Nanoparticles: Gold Coating and PEG Functionalization, J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol., 2013, 4, 222–228 CrossRef.
- A. M. Prantner, J. Chen, C. B. Murray and N. Scholler, Coating Evaluation and Purification of Monodisperse, Water-Soluble, Magnetic Nanoparticles Using Sucrose Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation, Chem. Mater., 2012, 24, 4008–4010 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Ling, K. Y. Wang and T.-S. Chung, Highly Water-Soluble Magnetic Nanoparticles as Novel Draw Solutes in Forward Osmosis for Water Reuse, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49, 5869–5876 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Iatridi, V. Georgiadou, M. Menelaou, C. Dendrinou-Samara and G. Bokias, Application of hydrophobically modified water-soluble polymers for the dispersion of hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticles inaqueous media, Dalton Trans., 2014, 43, 8633–8643 RSC.
- M. Irfan Majeed, Q. Lu, W. Yan, Z. Li, I. Hussain, M. Nawaz Tahir, W. Tremele and B. Tan, Highly water-soluble magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for drug delivery: enhanced in vitro therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin and MION conjugates, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013, 1, 2874–2884 RSC.
- S. Küçükdermenci, D. Kutluay, E. Çelik, Ö. Mermer and Ý. Avgýn, Concentration and path-length dependence of the Faraday rotation of magnetic fluids based on highly water-soluble Fe3O4/PAA nanoparticles synthesized by a high-temperature hydrolysis method, Mater. Technol., 2013, 47(3), 323–327 Search PubMed.
- H. Y. Koo, S. T. Chang, W. S. Choi, J.-H. Park, D.-Y. Kim and O. D. Velev, Emulsion-Based Synthesis of Reversibly Swellable, Magnetic Nanoparticle-Embedded Polymer Microcapsules, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 3308–3313 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Cheng, S. Liu, H. Gao, W. Tremel, N. Ding, R. Liu, P. W. Beines and W. Knoll, A Facile Approach for Transferring Hydrophobic Magnetic Nanoparticles into Water-Soluble Particles, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2008, 209, 1145–1151 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Khan, Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles embedded in microgels, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, 898–902 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Aqil, S. Vasseur, E. Duguet, C. Passirani, J. P. Benoît, A. Roch, R. Müller, R. Jérôme and C. Jérôme, PEO coated magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical application, Eur. Polym. J., 2008, 44(10), 3191–3199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, T. C. Hughes, B. W. Muir, L. J. Waddington, T. R. Gengenbach, C. D. Easton, T. M. Hinton, B. A. Moffat, X. Hao and J. Qiu, Water-dispersible magnetic carbon nanotubes as T2-weighted MRI contrast agents, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 378–386 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Robinson, C. Alexander, L. D. Tung, D. G. Fernig and N. T. K. Thanh, Fabrication of water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles by ligand-exchange with thermo-responsive polymers, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2009, 321, 1421–1423 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nidhin, R. Indumathy, K. J. Sreeram and B. Unni Nair, Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles of narrow size distribution on polysaccharide templates, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2008, 31(1), 93–96 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Lv, K. Li and Y. Li, Surface modification of quantum dots and magnetic nanoparticles with PEG-conjugated chitosan derivatives for biological applications, Chem. Pap., 2013, 67(11), 1404–1413 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Skaat and S. Margel, Newly Designed Magnetic and Non-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Potential Diagnostics and Therapy of Alzheimer's Disease, J. Biotechnol. Biomater., 2013, 3(2), 1000156 Search PubMed , 8 pp.
- N. Hoang Hai, N. Hoang Luong, N. Chau and N. Quy Tai, Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles embedded in polystyrene microspheres, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2009, 187, 012009 CrossRef.
- Z. Li, P. Wei Yi, Q. Sun, H. Lei, H. Li Zhao, Z. Hua Zhu, S. C. Smith, M. Bo Lan and G. Qing (Max) Lu, Ultrasmall Water-Soluble and Biocompatible Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Positive and Negative Dual Contrast Agents, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 2387–2393 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Thanh, Surface modification of iron oxide nanoparticles and their conjuntion with water soluble polymers for biomedical application, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2009, 187, 012046 CrossRef.
- V. M. Chakka, B. Altuncevahir, Z. Q. Jin, Y. Li and J. P. Liu, Magnetic nanoparticles produced by surfactant-assisted ball milling, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 99, 08E912 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. L. Iconaru, A. Mihaela Prodan, M. Motelica-Heino, S. Sizaret and S. Predoi, Synthesis and characterization of polysaccharide-maghemite composite nanoparticles and their antibacterial properties, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2012, 7, 576 CrossRef PubMed , 8 pp.
- J. Xie, C. Xu, N. Kohler, Y. Hou and S. Sun, Controlled PEGylation of Monodisperse Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Reduced Non-Specific Uptake by Macrophage Cells, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 3163–3166 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Cai and J. Wan, Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles in liquid polyols, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 305, 366–370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wan, W. Cai, X. Meng and E. Liu, Monodisperse water-soluble magnetite nanoparticles prepared by polyol process for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging, Chem. Commun., 2007, 5004–5006 RSC.
- G. Baldi, G. Lorenzi and C. Ravagli, Hyperthermic effect of magnetic nanoparticles under electromagnetic field, Process. Appl. Ceram., 2009, 3(1–2), 103–109 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Amstad, S. Zurcher, A. Mashaghi, J. Y. Wong, M. Textor and E. Reimhult, Surface Functionalization of Single Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Small, 2009, 5(11), 1334–1342 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhao, B. Zhang and L. Feng, Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles, Mater. Lett., 2012, 68, 112–114 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-M. Yang, K. Woo Lee and J. Kwon Moon, Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles as a draw solute in forward osmosis membrane process for the treatment of radioactive liquid waste, Transactions of the Korean Nuclear Society Spring Meeting Gwangju, Korea, May 30–31, 2013 Search PubMed.
- E. A. Osborne, T. M. Atkins, D. A. Gilbert, S. M. Kauzlarich, K. Liu and A. Y. Louie, Rapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Nanotechnology, 2012, 23(21), 215602 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Wang, J. Li, Q. Jiang and L. Zhao, Water-soluble Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high solubility for removal of heavy-metal ions from waste water, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 4544–4551 RSC.
- S. Xuan, L. Hao, W. Jiang, X. Gong, Y. Hua and Z. Chen, Preparation of water-soluble magnetite nanocrystals through hydrothermal approach, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, 308, 210–213 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L. Vander Elst and R. N. Muller, Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 2064–2110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. P. Chen, Y. Zhang, K. Xu, R. Z. Xu, J. W. Liu and N. Gu, Stability of Hydrophilic Magnetic Nanoparticles Under Biologically Relevant Conditions, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2008, 8, 6260–6265 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Sen, S. Magdassi, G. Nizri and I. J. Bruce, Dispersion of magnetic nanoparticles in suspension, Micro Nano Lett., 2006, 1(1), 39–42 CAS.
- S. Kumar, C. Ravikumar and R. Bandyopadhyaya, State of Dispersion of Magnetic Nanoparticles in an Aqueous Medium: Experiments and Monte Carlo Simulation, Langmuir, 2010, 26(23), 18320–18330 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. R. Dave and X. Gao, Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles for biodetection, imaging, and drug delivery: a versatile and evolving technology, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol., 2009, 1, 583–609 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Cui, S. Belo, D. Krüger, Y. Yan, R. T. M. de Rosales, M. Jauregui-Osoro, H. Ye, S. Su, D. Mathe, N. Kovács, I. Horváth, M. Semjeni, K. Sunassee, K. Szigeti, M. A. Green and P. J. Blower, Aluminium hydroxide stabilised MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as dual-modality contrasts agent for MRI and PET imaging, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 5840–5846 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Dickson, G. Liu, C. Li, G. Tachiev and Y. Cai, Dispersion and stability of bare hematite nanoparticles: effect of dispersion tools, nanoparticle concentration, humic acid and ionic strength, Sci. Total Environ., 2012, 419, 170–177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Stuyven, Q. Chen, W. Van de Moortel, H. Lipkens, B. Caerts, A. Aerts, L. Giebeler, B. Van Eerdenbrugh, P. Augustijns, G. Van den Mooter, J. Van Humbeeck, J. Vanacken, V. V. Moshchalkov, J. Vermantc and J. A. Martens, Magnetic field assisted nanoparticle dispersion, Chem. Commun., 2009, 47–49 RSC.
- K. Kendall and M. R. Kosseva, Nanoparticle aggregation influenced by magnetic fields, Colloids Surf., A, 2006, 286, 112–116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Scott, Y. Beabout, R. J. Wydra, M. Dan, R. Yokel, J. Z. Hilt and Y. Bae, Block Copolymer Self-assembled and Cross-linked Nanoassemblies for Combination Delivery of Iron Oxide and Doxorubicin, J. Appl. Pharm. Sci., 2013, 3(06), 021–028 CAS.
- R. Thomas, I.-K. Park and Y. Yeon Jeong, Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Multimodal Imaging and Therapy of Cancer, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2013, 14, 15910–15930 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, J. Li, W. Sun, Y. Hu, G. Zhang, M. Shen and X. Shi, Hyaluronic Acid-Modified Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for MR Imaging of Surgically Induced Endometriosis Model in Rats, PLoS One, 2014, 9(4), e94718 Search PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |