piRNA identification based on motif discovery†
Abstract
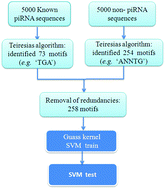
Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) is a class of small non-coding RNAs about 24 to 32 nucleotides long, associated with PIWI proteins, which are involved in germline development, transposon silencing, and epigenetic regulation. Identification of piRNA loci on the genome is very useful for further studies in the biogenesis and function of piRNAs. To accomplish this, we applied the computational biology tool Teiresias to identify motifs of variable length appearing frequently in mouse piRNA and non-piRNA sequences, respectively, and then proposed an algorithm for piRNA identification based on motif discovery, termed “Pibomd” by using these sequence motifs as features in the Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm, a sensitivity of 91.48% and a specificity of 89.76% on a mouse test dataset could be achieved, much better results than those reported in previously published algorithms. We also trained an unbalanced SVM classifier (named as “Asym-Pibomd”) that provided a higher specificity (96.2%) and a lower sensitivity (72.68%) than Pibomd. Inspite of the predicted ACC being less than that of Pibomd, the predicted ACC (84.44%) of Asym-Pibomd is about ten percent more than that obtained using the k-mer method. Further analysis of the motif positions on the piRNA sequences showed that the piRNA sequences may contain information at the 5′- and/or 3′-end recognized by the piRNA processing apparatus of actual piRNA precursors. Furthermore, this prediction method can be found on a user-friendly web server found at http://app.aporc.org/Pibomd/.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...