Acid monolayer functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles as catalysts for carbohydrate hydrolysis†
Abstract
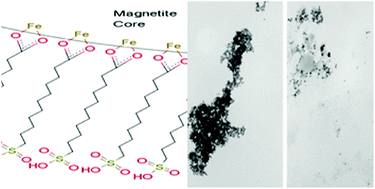
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles were functionalized with a quasi-monolayer of 11-sulfoundecanoic acid and 10-phosphono-1-decanesulfonic acid ligands to create separable solid acid catalysts. The ligands are bound through carboxylate or phosphonate bonds to the magnetite core. The ligand-core bonding surface is separated by a hydrocarbon linker from an outer surface with exposed sulfonic acid groups. The more tightly packed monolayer of the phosphonate ligand corresponded to a higher sulfonic acid loading by weight, a reduced agglomeration of particles, a greater tendency to remain suspended in solution in the presence of an external magnetic field, and a higher catalytic activity per sulfonic acid group. The particles were characterized by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), potentiometric titration, diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS), inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). In sucrose catalysis reactions, the phosphonic–sulfonic nanoparticles (PSNPs) were seen to be incompletely recovered by an external magnetic field, while the carboxylic–sulfonic nanoparticles (CSNPs) showed a trend of increasing activity over the first four recycle runs. The activity of the acid-functionalized nanoparticles was compared to the traditional solid acid catalyst Amberlyst-15 for the hydrolysis of starch in aqueous solution. Catalytic activity for starch hydrolysis was in the order PSNPs > CSNPs > Amberlyst-15. Monolayer acid functionalization of iron oxides presents a novel strategy for the development of recyclable solid acid catalysts.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Conversion of biomass with heterogeneous catalysts

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...