Photodegradation routes of the herbicide bromoxynil in solution and sorbed on silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
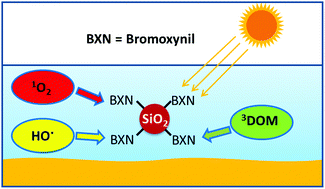
Some organic contaminants dissolved in natural waters tend to adsorb on suspended particles and sediments. In order to mimic the photodegradation routes in natural waters of bromoxynil (BXN) adsorbed on silica, we here prepare and characterize silica nanoparticles modified with BXN (NP-BXN). We measure the direct photolysis quantum yield of aqueous BXN at 307 nm (0.064 ± 0.001) and detect the formation of bromide ions as a reaction product. Under similar conditions the photolysis quantum yield of BXN bonded to NP-BXN is much lower (0.0021 ± 0.0004) and does not lead to formation of bromide ions. The rate constant of the reaction of NP-BXN with the excited triplet states of riboflavin, a molecule employed as a proxy of chromophore dissolved organic matter (DOM) was measured in laser flash-photolysis experiments. The rate constants for the overall (kt) and chemical interaction (kr) of singlet oxygen with NP-BXN were also measured. Kinetic computer simulations show that the relevance of the direct and indirect (through reactions with reactive species generated in photoinduced processes) photodegradation routes of BXN is very much affected by sorption on silica. Immobilization of the herbicide on the particles, on one hand, affects the photolysis mechanism and lowers its photolysis quantum yield. On the other hand, the results obtained in aqueous suspensions indicate that immobilization also lowers the rate of collisional encounter, which affects the quenching rate constants of excited triplet states and singlet oxygen with the herbicide.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Aquatic photochemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...