Using beryllium bonds to change halogen bonds from traditional to chlorine-shared to ion-pair bonds†
Abstract
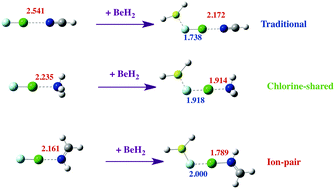
Ab initio MP2/aug′-cc-pVTZ calculations have been carried out to investigate the structures, binding energies, and bonding characteristics of binary complexes HFBe:FCl, R2Be:FCl, and FCl:N-base, and of ternary complexes HFBe:FCl:N-base and R2Be:FCl:N-base for R = H, F, Cl; N-base = NH3, NHCH2, NCH. Dramatic synergistic cooperative effects have been found between the Be⋯F beryllium bonds and the Cl⋯N halogen bonds in ternary complexes. The Cl⋯N traditional halogen bonds and the Be⋯F beryllium bonds in binary complexes become significantly stronger in ternary complexes, while the F–Cl bond weakens. Charge-transfer from F to the empty p(σ) orbital of Be leads to a bending of the XYBe molecule and a change in the hybridization of Be, which in the limit becomes sp2. As a function of the intrinsic basicity of the nitrogen base and the intrinsic acidity of the Be derivative, the halogen-bond type evolves from traditional to chlorine-shared to ion-pair bonds. The mechanism by which an ion-pair complex is formed is similar to that involved in the dissociative proton attachment process. EOM-CCSD spin–spin coupling constants 1XJ(Cl–N) across the halogen bond in these complexes also provide evidence of the same evolution of the halogen-bond type.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...