A novel approach for analyzing electrochemical properties of mixed conducting solid oxide fuel cell anode materials by impedance spectroscopy
Abstract
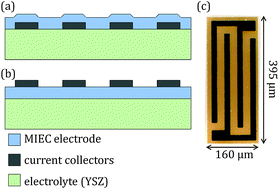
For application of acceptor-doped mixed conducting oxides as solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anodes, high electrochemical surface activity as well as acceptable electronic and ionic conductivity are crucial. In a reducing atmosphere, particularly the electronic conductivity of acceptor-doped oxides can become rather low and the resulting complex interplay of electrochemical reactions and charge transport processes makes a mechanistic interpretation of impedance measurements very complicated. In order to determine all relevant resistive and capacitive contributions of mixed conducting electrodes in a reducing atmosphere, a novel electrode design and impedance-based analysis technique is therefore introduced. Two interdigitating metallic current collectors are placed in a microelectrode, which allows in-plane measurements within the electrode as well as electrochemical measurements versus a counter electrode. Equivalent circuit models for quantifying the spectra of both measurement modes are developed and applied to simultaneously fit both spectra, using the same parameter set. In this manner, the electronic and ionic conductivity of the material as well as the area-specific resistance of the surface reaction and the chemical capacitance can be determined on a single microelectrode in a H2–H2O atmosphere. The applicability of this new tool was demonstrated in SrTi0.7Fe0.3O3−δ (STFO) thin film microelectrodes, deposited on single-crystalline yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) substrates. All materials parameters that contribute to the polarization resistance of STFO electrodes in a reducing atmosphere could thus be quantified.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...