Synthesis of diketopyrrolopyrrole based copolymers via the direct arylation method for p-channel and ambipolar OFETs†
Abstract
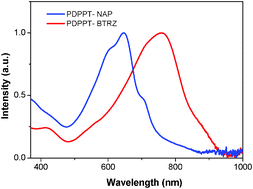
In this paper, we have synthesized two novel diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) based donor–acceptor (D–A) copolymers poly{3,6-dithiophene-2-yl-2,5-di(2-octyl)-pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione-alt-1,5-bis(dodecyloxy)naphthalene} (PDPPT-NAP) and poly{3,6-dithiophene-2-yl-2,5-di(2-butyldecyl)-pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione-alt-2-dodecyl-2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole} (PDPPT-BTRZ) via direct arylation organometallic coupling. Both copolymers contain a common electron withdrawing DPP building block which is combined with electron donating alkoxy naphthalene and electron withdrawing alkyl-triazole comonomers. The number average molecular weight (Mn) determined by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) for polymer PDPPT-NAP is around 23 400 g mol−1 whereas for polymer PDPPT-BTRZ it is 18 600 g mol−1. The solid state absorption spectra of these copolymers show a wide range of absorption from 400 nm to 1000 nm with optical band gaps calculated from absorption cut off values in the range of 1.45–1.30 eV. The HOMO values determined for PDPPT-NAP and PDPPT-BTRZ copolymers from photoelectron spectroscopy in air (PESA) data are 5.15 eV and 5.25 eV respectively. These polymers exhibit promising p-channel and ambipolar behaviour when used as an active layer in organic thin-film transistor (OTFT) devices. The highest hole mobility measured for polymer PDPPT-NAP is around 0.0046 cm2 V−1 s−1 whereas the best ambipolar performance was calculated for PDPPT-BTRZ with a hole and electron mobility of 0.01 cm2 V−1 s−1 and 0.006 cm2 V−1 s−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...