Fragment based electronic structural analysis of l-phenylalanine using calculated ionization spectroscopy and dual space analysis†
Abstract
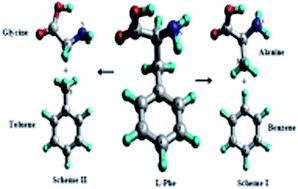
Two sets of amino acid-containing fragment schemes, the alanine/benzene scheme and the glycine/toluene scheme, are employed to study the electronic structure of an aromatic amino acid, L-phenylalanine (Phe). The calculated ionization energies (IEs) and the theoretical momentum distributions (TMDs) of the valence orbitals for the related molecules are analyzed to reveal the intra-molecular interactions through the fragments-in-molecules scheme. Density functional theory (DFT) based and Green function based quantum mechanical calculations as well as available experimental measurements are used in this study. It is found that the strong chemical bonding character of Phe seems to appear in the middle valence region of 11–20 eV, which largely shows the dependency of the fragment schemes. The valence energy region of 14 < IE < 20 eV in Phe is dominated by the glycine/toluene scheme, whereas the valence space of 11 < IE < 14 eV is dominated by the alanine/benzene scheme. The innermost valence space (i.e. IE > 20 eV) and the outermost valence space (i.e. the frontier orbitals) are less affected by the fragment schemes. These observations are confirmed using combined information on the position and momentum spaces in dual space analysis (DSA).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...