Plasmonic aptamer–gold nanoparticle sensors for small molecule fingerprint identification†
Abstract
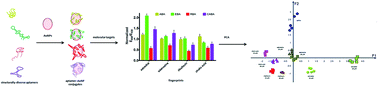
The utilization of the plasmonic response of aptamer–gold nanoparticle conjugates (Apt–AuNPs) to design cross-reactive arrays for fingerprint identification of small molecular targets was demonstrated for the first time. Four aptamers with different structural features previously selected to bind different targets were used in combination with AuNPs by adsorbing the DNA on the AuNPs surface. The optimized response of the Apt–AuNPs to the analytes showed that, depending on the specific aptamer used, target binding by the aptamer could result in an increase or decrease of Apt–AuNPs stability. These Apt–AuNPs showed the ability to recognize different analytes with different affinities, generating fingerprints that allowed unambiguous analyte identification with response times in less than fifteen minutes. Importantly, it was observed that it was not necessary to select an aptamer per analyte of interest to generate differentiable signatures, but a subset of aptamers could be used to identify a larger number of analytes. The data was analyzed using principal component analysis, showing efficient clustering of the different datasets for qualitative and quantitative identification. This work opens the door to using these Apt–AuNPs in point of care diagnostics applications where fast sensors with easy to read outputs are needed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...