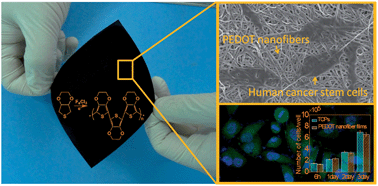
The development of modern biomedical nanotechnology requires conductive polymeric nanofibers with excellent mechanical and biocompatible properties to meet the needs of practical applications in complex biological systems. In the study, we developed a novel facile method to fabricate poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) nanofiber mats by electrospinning combined with in situ interfacial polymerization. The PEDOT nanofiber mats displayed superior mechanical properties (tensile strength: 8.7 ± 0.4 MPa; Young's modulus: 28.4 ± 3.3 MPa) and flexibility, which can almost be restored to its original shape even after serious twisting and crimping. Especially, from the results of the cellular morphology and proliferation of human cancer stem cells (hCSCs) cultured on the PEDOT nanofiber mats for 3 days, evidence was provided that the PEDOT nanofiber mats have similar biocompatibility to tissue culture plates (TCPs). Combined with an outstanding electrical conductivity of 7.8 ± 0.4 S cm−1, these excellent mechanical and biocompatible properties make the PEDOT nanofiber mats promising candidates in biotechnology applications, such as electroactive substrates/scaffolds for tissue engineering, drug delivery, cell culture, and implanted electrodes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...