The effect of common bacterial growth media on zinc oxide thin films: identification of reaction products and implications for the toxicology of ZnO
Abstract
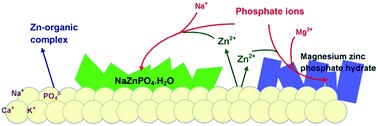
This study provides a thorough investigation on the effects of the commonly-employed microbial growth medium, namely the peptide-containing luria-bertani broth, tryptic soy broth, the glucose-containing M9 Minimal Salts Media as well as phosphate-buffered saline solution on the dissolution and microstructural transformation of zinc oxide thin film. Morphology and chemical composition of the ZnO film after incubation in the media was thoroughly characterised. In addition, the amount and rate of soluble zinc released by the ZnO thin films was quantified. Exposure of ZnO thin film in the different growth media saw formation of new zinc compounds, resulting from various chemical reactions of zinc with the medium components. Deposition of the new zinc compounds on top of the thin film caused morphological transformation of the film. Zinc leaching was observed in all of the tested media, with significantly higher extent of dissolution observed in peptide-containing organic media, such as luria bertani and tryptic soy broth. Complex organic components, such as amino acids and peptides form complexes with zinc oxide coatings, resulting in complexation-mediated leaching of zinc. Soluble zinc re-precipitates with components in the media, and therefore substantially reduced the amount of dissolved zinc. The results suggest strong influence of solution chemistry on ZnO speciation in a test medium, which have important implications for the mechanistic interpretation of ZnO toxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...