Thin-film microfabricated nanofluidic arrays for size-selective protein fractionation†
Abstract
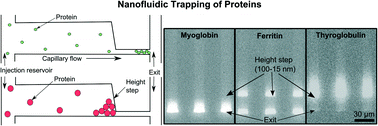
Size-selective fractionation and quantitation of biostructures in the sub-hundred nanometer size range is an important research area. Unfortunately, current methods for size fractionation are complex, time consuming, or offer poor resolution. Using standard microfabrication technology, we developed a nanofluidic sieving system to address these limitations. Our setup consists of an array of parallel nanochannels with a height step in each channel, an injection reservoir, and a waste reservoir. The height steps can size fractionate a protein mixture as a solution flows through the nanochannels via capillary action. We tested this system with different sizes and concentrations of five proteins to understand protein size and height step effects on trapping. Our results clearly show size-dependent trapping of proteins at nanometer-scale height steps in nanochannels. We also developed a model that predicts the observed size-dependent trapping of proteins. This work is a key step towards scalable nanofluidic methods for molecular fractionation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...