Assessment of entanglement features and dynamics from atomistic simulations and experiments in linear and short chain branched polyolefins
Abstract
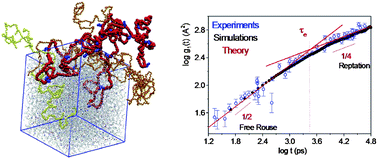
We report on full atomistic computer simulations of the molecular dimensions and dynamics of molten entangled linear and short chain branched polyethylene chains of the same length with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...