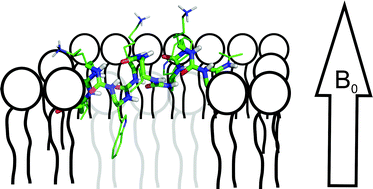
Synthetic oligomers that are derived from natural polypeptide sequences, albeit with unnatural building blocks, have attracted considerable interest in mimicking bioactive peptides and proteins. Many of those compounds adopt stable folds in aqueous environments that resemble protein structural elements. Here we have chemically prepared aliphatic oligoureas and labeled them at selected positions with 15N for structural investigations using solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In the first step, the main tensor elements and the molecular alignment of the 15N chemical shift tensor were analyzed. This was possible by using a two-dimensional heteronuclear chemical shift/dipolar coupling correlation experiment on a model compound that represents the chemical, and thereby also the chemical shift characteristics, of the urea bond. In the next step 15N labeled versions of an amphipathic oligourea, that exert potent antimicrobial activities and that adopt stable helical structures in aqueous environments, were prepared. These compounds were reconstituted into oriented phospholipid bilayers and the 15N chemical shift and 1H-15N dipolar couplings of two labeled sites were determined by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. The data are indicative of an alignment of this helix parallel to the membrane surface in excellent agreement with the amphipathic character of the foldamer and consistent with previous models explaining the antimicrobial activities of α-peptides.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...