An enhanced capillary electrophoresis method for characterizing natural organic matter†
Abstract
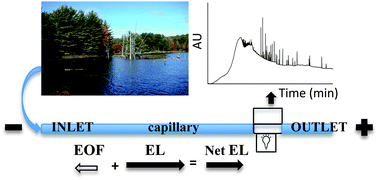
Natural organic matter (NOM) is ubiquitous and is one of the most complex naturally occurring mixtures. NOM plays an essential role in the global carbon cycle; atmospheric and natural

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...