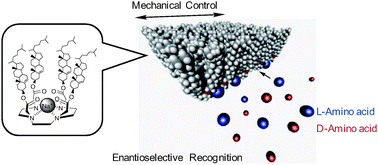
The cholesterol-armed cyclen Na+ complex formed stable Langmuir monolayers at the air–water interface. The π–A isotherm displayed a reasonable limiting molecular area of ∼1.57 nm2 and the areas expanded when amino acids were dissolved in water, indicating the efficient accommodation in the monolayers. Brewster angle microscopy (BAM) images exhibited almost no defects of the compressed Langmuir monolayers regardless of the presence of amino acids. Based on the idea that the increase in the limiting molecular areas corresponds to the amount of the adsorbed amino acid, the binding constants of three enantiomeric amino acids, namely valine (Val), leucine (Leu), and phenylalanine (Phe), were calculated at different surface pressures. Remarkably, a surface pressure dependent enantioselectivity of amino acid recognition was observed. Upon compression of the monolayers, the binding constants of amino acids increased accompanying an inversion of chiral selectivity from the D- to L-form in the case of Val and, conversely, from L- to D-form in the case of Phe.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...