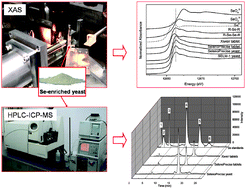
Selenium (Se)-enriched yeast has probably been the most widely investigated food supplement and the literature on Se speciation in the Se-enriched yeast is fairly abundant, however, the strategy for Se speciation commonly requires complicated pretreatment procedures such as digestion and stepwise extraction. The present study was carried out to apply X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) for the direct speciation of Se species with minimal pretreatment steps. By comparison of the XAS spectra of Se-enriched yeast samples with that of the standard Se species, organic R–Se–R (represented by selenomethionine) was found to be the main chemical form of Se. Quantitative speciation through principal component analysis (PCA) and least-squares linear combination (LC) fitting the Se-enriched yeast samples found 83%, 85% and 81% of R–Se–R (probably selenomethionine which is known to exist in yeast) for SelenoPrecise® yeast, SelenoPrecise® tablets, and Xiweir® tablets, respectively, which is in agreement with those from HPLC-ICP-MS analysis. More broadly, XAS can also be applied to other Se-enriched products with the merit of minimal pretreatment. However since XAS, specifically XANES, can only identify the chemical type rather than specific molecules, other methods like HPLC-ICP-MS are necessary to give not only the coordination environment of Se but also the identity of the Se species.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...