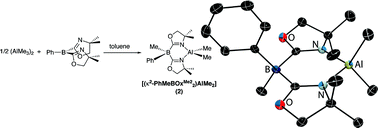
A compound that contains a Lewis acidic boron center and coordinating oxazoline groups, bis(4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazolinyl)phenylborane (PhB(OxMe2)2; 1), has been prepared and spectroscopically characterized. Solvent dependent 15N and 11B NMR spectroscopic properties and solid-state 11B NMR measurements provide support for intermolecular interactions involving Lewis acid and base sites. The bifunctional nature of oxazolinylborane 1 is demonstrated by its reaction with (AlMe3)2, which proceeds via methide abstraction by the boron and oxazoline coordination to aluminum to yield [(κ2-PhMeB(OxMe2)2AlMe2] (2). Compound 2 contains a planar six-membered chelate ring, in contrast to related bis(pyrazolyl)boratoaluminum compounds that are puckered. Additionally, compound 2 and related bidentate tris(oxazolinyl)phenylborato dimethylaluminum are inert toward aluminum-methyl bond protonolysis. This robust nature suggested the possibility of using these oxazolinylboratoaluminum compounds in catalytic reactions, as is demonstrated by lactide ring-opening polymerization.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...