Weakly basic alkyldimethylamine oxide (CnDMAO, n = 12, 14, and 16) molecules can be protonated to form a cationic surfactant, CnDMAOH+, by an acidic fluorocarbon surfactant, 8-2-fluorotelomer unsaturated acid (C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH), to produce the salt-free cationic and anionic (catanionic) surfactant mixtures in aqueous solution. These comparative studies on phase behavior and rheological properties of these salt-free catanionic hydrocarbon–fluorocarbon surfactant mixtures in detail clearly indicate the existence of a birefringent Lα-phase for C12DMAO/C7F15CF
CHCOOH), to produce the salt-free cationic and anionic (catanionic) surfactant mixtures in aqueous solution. These comparative studies on phase behavior and rheological properties of these salt-free catanionic hydrocarbon–fluorocarbon surfactant mixtures in detail clearly indicate the existence of a birefringent Lα-phase for C12DMAO/C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH and C14DMAO/C7F15CF
CHCOOH and C14DMAO/C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH systems at 25.0 ± 0.1 °C. However, the birefringent Lα-phase of C16DMAO/C7F15CF
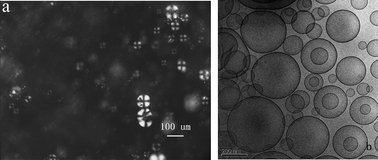
CHCOOH systems at 25.0 ± 0.1 °C. However, the birefringent Lα-phase of C16DMAO/C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH system exist at 60.0 ± 0.1 °C. The birefringent Lα-phase which consists of uni- and multilamellar vesicles, and oligovesicular vesicles is independent of the hydrocarbon chain of CnDMAO at controlled temperatures. The vesicles were demonstrated by cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) and negative-staining TEM images, in which pliability of the bilayer membranes decreases with the increasing length of hydrogenated chains of hydrocarbon surfactants. The formation of the salt-free catanionic Lα-phase consisting of vesicles could be induced by the strong electrostatic interaction between the cationic hydrocarbon C14DMAOH+ and the anionic fluorocarbon C7F15CF
CHCOOH system exist at 60.0 ± 0.1 °C. The birefringent Lα-phase which consists of uni- and multilamellar vesicles, and oligovesicular vesicles is independent of the hydrocarbon chain of CnDMAO at controlled temperatures. The vesicles were demonstrated by cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) and negative-staining TEM images, in which pliability of the bilayer membranes decreases with the increasing length of hydrogenated chains of hydrocarbon surfactants. The formation of the salt-free catanionic Lα-phase consisting of vesicles could be induced by the strong electrostatic interaction between the cationic hydrocarbon C14DMAOH+ and the anionic fluorocarbon C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOO−, C14DMAOH+ is produced through acid–base reaction of C14DMAO and C7F15CF
CHCOO−, C14DMAOH+ is produced through acid–base reaction of C14DMAO and C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH. The rheological properties of micelles and vesicles in the three mixture systems were measured, which provided much more information about the hydro- and fluorocarbon surfactant mixtures. The size distribution and structural transition of these similar systems but having different length chains of hydrocarbon surfactants were studied by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and 1H and 19F NMR spectroscopy.
CHCOOH. The rheological properties of micelles and vesicles in the three mixture systems were measured, which provided much more information about the hydro- and fluorocarbon surfactant mixtures. The size distribution and structural transition of these similar systems but having different length chains of hydrocarbon surfactants were studied by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and 1H and 19F NMR spectroscopy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH), to produce the salt-free cationic and anionic (catanionic)
CHCOOH), to produce the salt-free cationic and anionic (catanionic) ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH and C14DMAO/C7F15CF
CHCOOH and C14DMAO/C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH systems at 25.0 ± 0.1 °C. However, the birefringent Lα-phase of C16DMAO/C7F15CF
CHCOOH systems at 25.0 ± 0.1 °C. However, the birefringent Lα-phase of C16DMAO/C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH system exist at 60.0 ± 0.1 °C. The birefringent Lα-phase which consists of uni- and multilamellar vesicles, and oligovesicular vesicles is independent of the hydrocarbon chain of CnDMAO at controlled temperatures. The vesicles were demonstrated by
CHCOOH system exist at 60.0 ± 0.1 °C. The birefringent Lα-phase which consists of uni- and multilamellar vesicles, and oligovesicular vesicles is independent of the hydrocarbon chain of CnDMAO at controlled temperatures. The vesicles were demonstrated by ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOO−, C14DMAOH+ is produced through acid–base reaction of C14DMAO and C7F15CF
CHCOO−, C14DMAOH+ is produced through acid–base reaction of C14DMAO and C7F15CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHCOOH. The rheological properties of micelles and vesicles in the three mixture systems were measured, which provided much more information about the hydro- and
CHCOOH. The rheological properties of micelles and vesicles in the three mixture systems were measured, which provided much more information about the hydro- and 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...