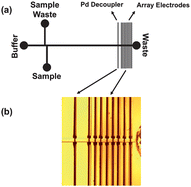
Selectivity and resolution for analyses conducted using microfluidic devices can be improved by increasing the total number of individual detection elements in the device. Here, a poly(dimethylsiloxane) capillary electrophoresis microchip was fabricated with an integrated electrode array for selective detection of small molecules. Eight individually addressable gold electrodes were incorporated in series after a palladium current decoupler in the separation channel of an electrophoresis microchip. The electrode array device was characterized using a mixture of biologically relevant analytes and xenobiotics: norepinephrine, 4-aminophenol, acetaminophen, uric acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. Separation efficiencies as high as 9000 ± 1000 plates (n = 3) for 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and limits of detection as low as 2.6 ± 1.2 µM (n = 3) for norepinephrine were obtained using this device. After characterizing the performance of the device, potential step detection was conducted at the array electrodes and selective detection achieved based upon differences in redox potentials for individual analytes. Utilization of potential step detection was particularly advantageous for resolving co-migrating species; resolution of 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine from acetaminophen using potential control was demonstrated. Finally, a human urine sample was analyzed using potential step detection to demonstrate the applicability of this device for complex sample analysis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...