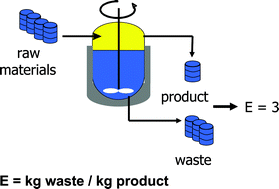
The development of green chemistry is traced from the introduction of the concepts of atom economy (atom utilisation) and E factors in the early 1990s. The important role of catalysis in reducing or eliminating waste is emphasised and illustrated with examples from heterogeneous catalytic oxidations with hydrogen peroxide, homogeneous catalytic oxidations and carbonylations and organocatalytic oxidations with stable N-oxy radicals. Catalytic reactions in non-conventional media, e.g. aqueous biphasic, supercritical carbon dioxide and ionic liquids, are presented. Biotransformations involving non-natural reactions of enzymes, e.g. ester ammoniolysis, and the rational design of semi-synthetic enzymes, such as vanadatephytase, are discussed. The optimisation of enzyme properties using in vitro evolution and improvement of their operational stability by immobilisation as cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEA®) are presented. The ultimate in green chemistry is the integration of catalytic steps into a one-pot, catalytic cascade process. An example of a chemoenzymatic synthesis of an enantiomerically pure amino acid in water and a trienzymatic cascade process using a triple-decker oxynitrilase/nitrilase/amidase CLEA are discussed. Finally, catalytic conversions of renewable raw materials are examined and the biocatalytic aerobic oxidation of starch to carboxy starch is presented as an example of green chemistry in optima forma i.e. a biocompatible product from a renewable raw material using a biocatalytic air oxidation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...