Biofunctionalisation of porous silicon (PS) surfaces by using homobifunctional cross-linkers
Abstract
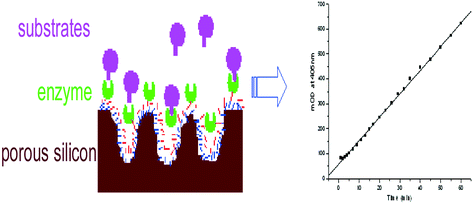
Porous silicon surfaces can be bio-functionalised by a simple three-step method. First the hydrogen-terminated porous silicon was oxidised and amino-silanised in a one-pot reaction by 3-aminopropyl(triethoxyl)silane with the aid of an organic base, diisopropylethylamine. Secondly, the primary amine reacted with either of two homobifunctional cross-linkers, bis(N-succinimidyl)carbonate and (N,N′-bis(p-maleimidophenyl)methylene. By modulating the reaction conditions, a high surface coverage of linking groups, succinimidyl ester or maleimide, can be obtained separately. Since homobifunctional cross-linkers can form bridged structures with both ends fixed to the surface, the reaction conditions were optimised for one end attached to the surface and the other end pendent. Succinimidyl ester is an amino-reactive group, therefore mouse monoclonal antibody bearing amino groups was grafted. An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay was used to evaluate the surface density of antibody at 0.008 ng cm−2. The other linker, (N,N′-bis(p-maleimidophenyl)methylene, was refluxed in acetonitrile with surface amines to result in maleimde-terminated surfaces. Then a reduced urokinase bearing accessible thiol groups was grafted and its enzymatic activity was assayed at 0.004 nmol cm−2 for urokinase. Transmission infrared, X-ray photoelectron, interferometric reflectance, UV-Vis, photoluminescence spectroscopies and a chromogenic assay were used to characterise the surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...