Pharmacognostic and pharmacological evaluation of Eulaliopsis binata plant extracts by measuring in vitro/in vivo safety profile and anti-microbial potential†
Abstract
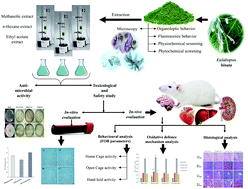
The present investigation emphasizes the pharmacognostic and phytochemical screening of Eulaliopsis binata and further evaluates the extracts of this plant for toxicological profile and anti-bacterial potential based on in vivo/in vitro assays. Microscopy, powder characteristics of the leaf material, and physicochemical and phytochemical screening were assessed for pharmacognostic evaluation. Dry leaves of Eulaliopsis binata were extracted using different solvents (methanol, ethyl acetate, and hexane), and the extracts obtained were further investigated for in vitro/in vivo toxicological study. Moreover, acute toxicity was assessed by evaluating the anti-oxidant defense system and anatomical damage in vital organs. In addition, anti-bacterial activity of all the extracts was assessed by the Kirby-Bauer method. Physicochemical and microscopic observations showed the unique identification mark for leaf powder and leaf transverse section. Phytochemical investigation evidenced the presence of flavonoids and phenolic contents in the methanolic extract. All extracts were found to be hemocompatible and exhibited no induction of behavioral alteration and no alteration in the anti-oxidant potential and anatomical structure of the vital organs. On the other hand, the methanolic extract showed a significant upsurge in the reduced glutathione level, whereas all extracts showed significant anti-bacterial potential in a dose-dependent manner. Eulaliopsis binata has inimitable pharmacognostical characteristics, good safety profile and significant anti-oxidant and anti-bacterial potential that show immense possibility for its further investigation for pharmacological use.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...