Amino-PAHs activated Nrf2/ARE anti-oxidative defense system and promoted inflammatory responses: the regulation of PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
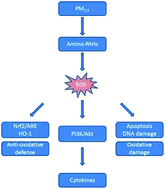
The amino polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (amino-PAHs) were frequently detected in PM2.5, and it was suggested that they contributed to the harmful health effects associated with PM2.5. However, the process through which amino-PAHs induce oxidative stress responses as well as the pro-inflammatory processes along with the associated mechanisms is still not well-known. In this study, oxidative stress level, Nrf2/ARE anti-oxidative defense responses, oxidative damages and cytokine expressions were investigated in the A549 cell line after it was treated with typical airborne amino-PAHs including 1-aminopyrene (1-AP) and 3-aminofluoranthene (3-AF). The possibility of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway participating in the regulation of cytokine gene expression was also considered, and the study was conducted accordingly. The results showed that 1-AP and 3-AF in a dose-dependent manner could cause extensive damages including cell apoptosis, cell cycle arrests, and DNA damages and could up-regulate the TNF-α gene expression. In addition, the Nr2/ARE defense system was activated, as evidenced by the increased protein expression levels and nuclear translocation of Nrf2. The Nrf2/ARE binding activity was elevated and was measured with the EMSA method. Also, the protein of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) was up-regulated. Finally, an increase in the protein expressions of the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and phosphorylation levels of Akt was observed, indicating that the PI3K/Akt pathway was activated. Furthermore, both LY294002 (an inhibitor of PI3K) and MK-2206 (an inhibitor of Akt) could significantly decrease the elevated TNF-α gene expressions, suggesting that the PI3K/Akt pathway was involved in the regulation of TNF-α expressions induced by 1-AP and 3-AF. Our results further confirmed that amino-PAHs could be a particularly important PAH derivatives contributing to the health risks caused by PM2.5.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Toxicology Research Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...