Evaluation of the toxic potential of arecoline toward the third instar larvae of transgenic Drosophila melanogaster (hsp70-lacZ) Bg9
Abstract
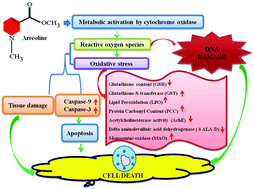
Arecoline is the key component of areca nut and has been suggested as a carcinogenic agent. In the present study, the third instar larvae of transgenic Drosophila melanogaster (hsp70-lacZ) Bg9 were allowed to feed on a diet having 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 μM arecoline for 24 h. After the completion of 24 h, the larvae were subjected to ONPG assay, X-gal staining, trypan blue exclusion test, oxidative stress markers, and apoptotic and comet assays. A dose-dependent increase in the β-galactosidase activity, tissue damage, glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity, lipid peroxidation assay, monoamine oxidase (MAO), caspase-9 and 3, protein carbonyl content (PCC), apoptotic index, and DNA damage and decrease in glutathione (GSH) content, delta aminolevulinic acid dehydrogenase (δ-ALA-D), and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity were observed in the larvae exposed to 20, 40 and 80 μM arecoline. The results suggest that arecoline is toxic at 20, 40, and 80 μM toward the third instar larvae of transgenic Drosophila melanogaster (hsp70-lacZ) Bg9. Arecoline did not show any toxic effects at 5 and 10 μM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...