Cytometrical analysis of the adverse effects of indican, indoxyl, indigo, and indirubin on rat thymic lymphocytes
Abstract
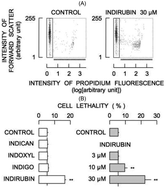
Many businesses thrive by producing health supplements from agricultural products, as exemplified by the production of functional (or health) foods using plants traditionally cultivated in rural areas. Dyes, such as indican, indigo, indoxyl, and indirubin, present in dye plants, possess antibacterial, antifungal, and antiproliferative activities. However, these effects may also lead to cytotoxicity. Thus, studies on normal mammalian cells are necessary to identify cytotoxicity and prevent adverse effects of functional foods that contain these dyes. In this study, the effects of indican, indigo, indoxyl, and indirubin were evaluated by flow cytometry using appropriate fluorescent probes in rat thymic lymphocytes. Among the dyes analyzed, indirubin exerted distinct cellular activities. Treatment with indirubin (10–30 μM) increased the population of shrunken dead cells. The side scatter, but not forward scatter, increased in indirubin-treated living cells. It increased the population of annexin V-bound living and dead cells and that of dead cells without annexin V. Indirubin elevated intracellular Ca2+, but not Zn2+ levels. The cellular content of superoxide anions increased and that of glutathione decreased. Indirubin depolarized the cellular plasma and mitochondrial membranes. It did not potentiate or attenuate the cytotoxicity of A23187 (Ca2+ overload) and H2O2 (oxidative stress). The results suggested that indirubin induces both apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death. It may be difficult to predict and prevent the adverse effects of indirubin due to its diverse activities on normal mammalian cells. Therefore, indirubin should be removed from products that contain dye plant extracts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...