A comparative study of hydrophilic phosphine hexanuclear rhenium cluster complexes’ toxicity
Abstract
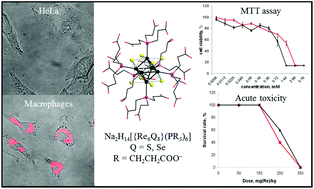
The octahedral rhenium cluster compound Na2H8[{Re6Se8}(P(C2H4CONH2)(C2H4COO)2)6] has recently emerged as a very promising X-ray contrast agent for biomedical applications. However, the synthesis of this compound is rather challenging due to the difficulty in controlling the hydrolysis of the initial P(C2H4CN)3 ligand during the reaction process. Therefore, in this report we compare the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of Na2H8[{Re6Se8}(P(C2H4CONH2)(C2H4COO)2)6] with those of related compounds featuring the fully hydrolysed form of the phosphine ligand, namely Na2H14[{Re6Q8}(P(C2H4COO)3)6] (Q = S or Se). Our results demonstrate that the cytotoxicity and acute in vivo toxicity of the complex Na2H8[{Re6Se8}(P(C2H4CONH2)(C2H4COO)2)6] solutions were considerably lower than those of compounds with the fully hydrolysed ligand P(C2H4COOH)3. Such behavior can be explained by the higher osmolality of Na2H14[{Re6Q8}(P(C2H4COO)3)6] versus Na2H8[{Re6Se8}(P(C2H4CONH2)(C2H4COO)2)6].


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...