A comparison of toxicity and toxicokinetics in rats and dogs following twenty-eight-day, repeat-dose oral administration of nifurtimox
Abstract
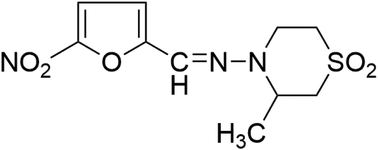
Nifurtimox has been an important treatment for trypanosomiasis for many years, but new research indicates that the drug may also be an effective therapy for malignant neuroblastoma. However, there have been few published reports evaluating the toxicity of nifurtimox in different species. Therefore, to further understand its toxicity and toxicokinetic profiles, Sprague Dawley rats and beagle dogs were orally administered nifurtimox at 0, 25, 75 and 150 mg kg−1 day−1, and 0, 30, 60 and 120 mg kg−1 day−1, respectively, for 28 days, which was followed by a 28-day recovery period. Significant decreases in the body weight and food consumption were observed in rats given 75 and 150 mg kg−1 day−1, but no significant difference was observed in either body weight or food consumption in dogs. No notable gender difference was observed in the rats in our study. The mean Cmax and AUC0–t increased with the exposure time in rats, and systemic exposure on day 28 was notably higher than that on day 1 for each dosing group. In contrast, in dogs the mean Cmax and AUC0–t increased significantly in the 120 mg kg−1 day−1 group only. Other findings in rats included a dose-dependent increase in total bilirubin and urea, a significant increase in the kidney organ coefficient, a decrease in heart and thymus weights, and a decrease in the weight of testes and epididymides tissue in males administered 75 and 150 mg kg−1 day−1, with dead sperms observed in the epididymides and a loss of necrotic cells. Furthermore, the brains of rats administered 150 mg kg−1 day−1 nifurtimox revealed cerebral tissue softening. In dogs there were no treatment-related changes in organ weights during the dosing period. However, deciduous spermatoblasts were observed in the seminiferous tubules and there was a lack of long sperms in the epididymides. The findings from this study demonstrate inter-species differences in nifurtimox toxicity and toxicokinetics. These results are relevant to the evaluation of the wider clinical applications of this drug.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...