Tuning the organic microcrystal laser wavelength of ESIPT-active compounds via controlling the excited enol* and keto* emissions†
Abstract
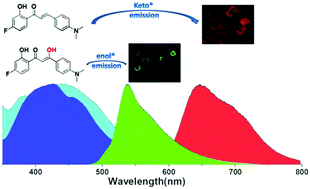
The excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) process provides a real four-level system, which forms the working basis of many laser dyes in solutions but remains largely unexplored in the solid-state gain medium. Herein, we modulated the keto* and enol* emissions by switching the intramolecular hydrogen-bond to the intermolecular hydrogen-bond in the solid-state for tuning the emission colors of ESIPT-microcrystal lasers. Both model compounds of 2′-hydroxychalcone derivatives of M1 and M2 exhibit very similar dual enol* and keto* emissions in the aprotic solvents, typical for ESIPT-active molecules. When aggregated into hexagonal-plate microcrystals (HPMCs), the intramolecular hydrogen-bond ensures the photoinduced proton tautomerization from enol* to keto* tautomers, resulting in intense red fluorescence of M1 HPMCs at 647 nm from the keto* form. In sharp contrast, the introduction of an extra hydroxyl group into M2 leads to the formation of an intermolecular hydrogen bond between two adjacent molecules, which suppresses the ESIPT process in the solid-state and therefore leads to intense green emission of M2 HPMCs at 537 nm from the enol* form. The solid-state photoluminescence efficiencies of HPMCs of M1 and M2 are as high as 42% and 51%, respectively. Moreover, well-faceted HPMCs of both M1 and M2 can function as whispering-gallery mode microresonators, enabling microlasers with very low laser thresholds of 10.8 μJ cm−2 for red-emissive M1-HPMCs and 9.4 μJ cm−2 for green emissive M2-HPMCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...