Discrete face-to-face stacking of anthracene inducing high-efficiency excimer fluorescence in solids via a thermally activated phase transition†
Abstract
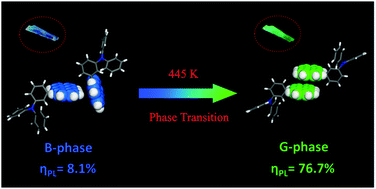
It is always a challenge for planar polycyclic aromatic molecules to achieve high efficiency in solids owing to their frequent encounter with aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ). An anthracene derivative with one-side meta-substituted triphenylamine (TPA) was found to show high-efficiency excimer fluorescence (ηPL = 76.8%) in G-phase (green) crystals as well as a long lifetime, in sharp contrast with that of a monomer in a doped film (ηPL = 36.6%) and that of B-phase (blue) crystals (ηPL = 8.1%). In essence, the excimer-induced enhanced emission can be ascribed to the special intermolecular stacking in the solid state, namely, discrete antiparallel dimeric stacks between anthracene moieties in G-phase crystals, which are responsible for greatly suppressed non-radiative deactivation due to a uniform emissive state preventing the formation of an energy-trapping “dark” state. Moreover, a G-phase could be obtained through a thermally-activated phase transition from B-phase crystals, corresponding to the completely synchronized change of fluorescence properties. The present results consolidate a novel strategy of designing discrete dimeric stacking of planar polycyclic aromatic molecules to achieve high-efficiency fluorescence in the solid state by an excimer-induced enhanced emission (EIEE) mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...