First observation of mutual energy transfer of Mn4+–Er3+via different excitation in Gd2ZnTiO6:Mn4+/Er3+ phosphors†
Abstract
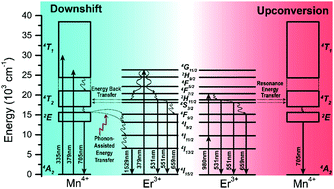
Mutual energy transfer between rare earth ions and transition metal ions in a single luminescence material easily achieves multifunctions by altering the excitation wavelength. In this study, we first observe the mutual energy transfer process between Mn4+ and Er3+via different excitations in Mn4+–Er3+ co-doped Gd2ZnTiO6 phosphors synthesized by a high temperature solid-state reaction. During the downshift energy transfer from Mn4+ to Er3+, the Gd2ZnTiO6:Mn4+/Er3+ phosphor exhibits a strong near-infrared emission around 1529 nm with a wide excitation band extending from 250 to 550 nm. Based on Dexter's theory, the energy transfer mechanism mainly contributes to a dipole–dipole interaction between Mn4+ and Er3+ ions, which is responsible for the greatly enhanced emission at 1529 nm. Upon the upconversion energy transfer from Er3+ to Mn4+, the Gd2ZnTiO6:Mn4+/Er3+ phosphor shows a deep red emission of Mn4+ under 980 nm laser excitation. The energy transfer process from Er3+ to Mn4+ is fully demonstrated by variations in excitation power as well as luminescence lifetimes of 551 nm emission of Er3+. Two-photon processes and resonance energy transfer from Er3+ to Mn4+ are required to populate the 2E emitting level of Mn4+.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...