Effect of laser energy on the crystal structure and UV response characteristics of mixed-phase MgZnO thin films deposited by PLD and the fabrication of high signal/noise ratio solar-blind UV detector based on mix-phase MgZnO at lower voltage
Abstract
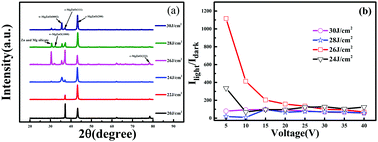
MgZnO thin films (with Mg0.4Zn0.6O as the target) were fabricated on fused quartz substrates employing PLD method under different laser energy densities. Cubic structured MgZnO thin films were made at laser energy densities of 20 J cm−2 and 22 J cm−2, whilst the MgZnO thin films were deposited along both cubic and hexagonal structures under higher laser energy density condition. When a higher energy density laser was focused on the MgZnO target during the deposition process, the MgZnO thin film was found to be deposited with a more hexagonal structure and a higher Zn composition. There are two response peaks located in the solar-blind UV and visible-blind UV regions within the UV response spectrum of the mixed-phase MgZnO based detector deposited at laser energy over 24 J cm−2. When the deposition laser energy density increased from 24 to 30 J cm−2, the maximum UV responsivity of the mixed-phase MgZnO-based detector increased from 0.06 A W−1 to 1 A W−1 at 40 V bias voltage, and the visible-blind UV response peak of the mix-phase MgZnO based detector was also higher due to the MgZnO adopting a more hexagonal structure; furthermore, a higher internal gain is obtained, which can be attributed to a higher density of interfaces between the MgZnO grains of different structures in the mixed-phase MgZnO thin film. At 5 V bias voltage, the Ilight(230 nm)/Idark ratio of the UV detector based on mix-phase MgZnO deposited at 24 J cm−2 reached 500, and the Ilight(290 nm)/Idark ratio of the UV detector based on mix-phase MgZnO deposited at 26 J cm−2 reached 1100. Therefore, the UV-detector based on mixed-phase MgZnO thin films is sensitive to solar-blind and visible-blind UV light with strong background noise (on Earth) when the boundaries between (111) an (200) cubic MgZnO makes obvious function in decreasing the dark current of the detectors at lower bias voltage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...