PEGMa modified molybdenum oxide as a NIR photothermal agent for composite thermal/pH-responsive p(NIPAM-co-MAA) microgels†
Abstract
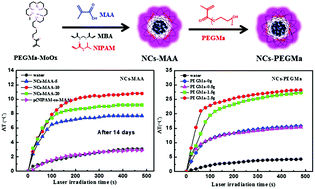
Molybdenum oxide nanomaterials have received increasing attention in recent years for their strong localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) absorption in the near-infrared (NIR) region and pH-dependent degradability. However, the rapid degradation of MoOx at physiological pH values would decrease the NIR photothermal effect. Here, we designed and prepared PEGMa–MoOx/p(NIPAM-co-MAA) microgels (NCs) exhibiting adjustable degradation. For that purpose, PEGMa (Mn = 400) modified MoOx was synthesized through a simple hydrothermal process. Then, PEGMa–MoOx with existing C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C groups was continually polymerized with NIPAM and MAA through emulsion polymerization. MAA was introduced to provide an acidic microenvironment (pH at 3–5) to control the degradation rate of PEGMa–MoOx. The photothermal efficiency of the NCs could be maintained at 54% even after 14 days. Meanwhile, the NCs also displayed a pH-dependent thermal response. Moreover, PEGMa was added again in the emulsion polymerization process to elevate the photothermal efficiency, and the irradiation result indicated that the NCs could increase the temperature by 27 °C. The complex microgel integrates pH/temperature/photothermal triple response characteristics and exhibits huge potential for chemo-photothermal combination cancer therapy.
C groups was continually polymerized with NIPAM and MAA through emulsion polymerization. MAA was introduced to provide an acidic microenvironment (pH at 3–5) to control the degradation rate of PEGMa–MoOx. The photothermal efficiency of the NCs could be maintained at 54% even after 14 days. Meanwhile, the NCs also displayed a pH-dependent thermal response. Moreover, PEGMa was added again in the emulsion polymerization process to elevate the photothermal efficiency, and the irradiation result indicated that the NCs could increase the temperature by 27 °C. The complex microgel integrates pH/temperature/photothermal triple response characteristics and exhibits huge potential for chemo-photothermal combination cancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...