Facile in situ synthesis of stable luminescent organic–inorganic lead halide perovskite nanoparticles in a polymer matrix†
Abstract
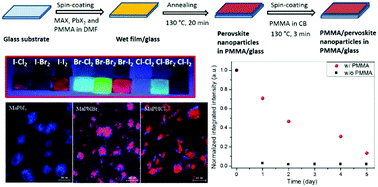
Organic–inorganic halide perovskites have attracted a lot of interest for applications such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs), photodetectors and lasers. As this group of materials is highly sensitive to moisture and oxygen, a simple in situ controlled synthesis of these nanoparticles (NPs) in a polymer matrix will open up the possibility for a wide range of light-emitting and color-conversion applications. This paper presents a simple in situ approach for controlled synthesis of organic–inorganic lead halide perovskite NPs as a function of halide composition in polymer matrix (polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA). Chemical mapping using scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) shows a varying of size distribution of the lead halide perovskite NPs. Mixed halide NP in PMMA were composed of grains of different compositions. Time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) correlated with compositional information from energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) provides evidence for the role of surfaces and grain boundaries on charge recombination in the nanoparticles. The annealing temperature and the molar ratio of the precursors were found to greatly affect the morphology and composition of the perovskite NP in polymer matrix.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...