Self-stripping of free-standing microparticle gel membranes driven by asymmetric swelling†
Abstract
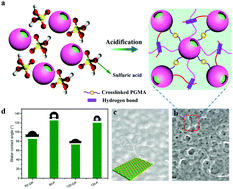
Free-standing nanoparticle membranes, which are composed of inorganic nanoparticles and organic ligands, have attracted a lot of attention because of their excellent physical chemical properties and widespread applications such as in sensors, photonic crystals and SERS substrates. However, the self-assembly of micro-sized particles into a free-standing microparticle membrane, particularly actuated membranes, is still a burning challenge. Herein, we propose the concept of “microparticle gels” fully formed by anisotropic (core–satellite, yolk–shell) microparticles and design an uncustomary strategy that transforms micro-sized particles into microparticle gels by an acidification process. The as-prepared microparticle gels possess excellent film-forming properties, which benefit from chemical cross-linking and hydrogen bonding of open-loop epoxy groups. They are able to embed in a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate at 120 °C to form a composite membrane with remarkable swelling properties. In addition, free-standing double-layered microparticle gel/PET membranes were formed on various substrates at lower temperatures with excellent self-stripping properties driven by asymmetric swelling in water. The self-stripping process can be controlled by salt concentration and stopped at a salt concentration of 25%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...