Resistive switching phenomena induced by the heterostructure composite of ZnSnO3 nanocubes interspersed ZnO nanowires
Abstract
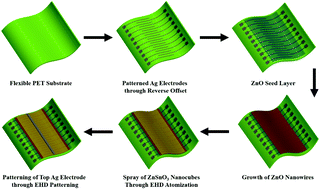
The resistive switching effect of various materials has been investigated because of their promising advantages such as high scalability, low cost, simple structure and less power consumption of such memory devices. In this study, the resistive switching effect in nanocomposites of zinc oxide nanowires (ZnO NWs) and zinc stannate nanocubes (ZnSnO3 NCs) has been explored. The device was fabricated on a flexible poly(ethylene terephthalate) substrate on which highly conductive (0.3 Ω cm) patterns of silver (Ag) were deposited as bottom electrodes using a reverse offset printing technique. Vertically aligned and highly dense ZnO NWs were grown on the Ag patterns using hydrothermal synthesis followed by spraying of ZnSnO3 NCs using an electrohydrodynamic atomization (EHDA) technique. Finally, the top Ag electrode was patterned using an EHD patterning technique to complete the fabrication of the device. The fabricated device exhibited bipolar and rewritable characteristics, and had a nonvolatile resistive switching memory with an off/on ratio of 5.8 × 102 and a retention time of 104 s at a small operating voltage (1.2 V). The electrical results obtained with the Ag–ZnO/ZnSnO3–Ag memory device were remarkable and they showed significant repeatability. The significantly stable, highly durable and promising results obtained with the ZnO NWs–ZnSnO3 NCs heterostructure make this semiconductive nanocomposite a potential candidate for use in future flexible memory devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...