Application of composition controlled nickel-alloyed iron sulfide pyrite nanocrystal thin films as the hole transport layer in cadmium telluride solar cells†
Abstract
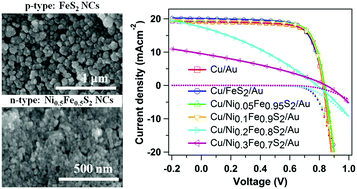
Here, we report hot-injection colloidal synthesis, characterization, and control of electronic conductivity of nickel-alloyed iron sulfide (NixFe1−xS2) pyrite nanocrystals (NCs). The Ni-alloyed iron pyrite NCs were synthesized using iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni) bromides as Fe and Ni sources, and elemental sulfur (S) as a sulfur source. As Ni is incorporated into the iron pyrite (FeS2) NCs, the X-ray diffraction (XRD) peaks shift towards lower diffraction angles indicating higher lattice constants of the alloyed NCs in accord with Vegard's law. Scherrer-analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging indicate that the average particle sizes of alloyed NCs are smaller compared to pure FeS2 NCs. In UV-Vis-NIR spectra, the alloyed NCs have higher absorbance in the infrared (IR) region than pure FeS2 NCs indicating Ni-alloyed NCs have higher densities of mid-band gap defect states. Based on thermal probe and Hall-effect measurements, the majority charge carriers in these alloyed NCs depend upon the material composition. Pure iron pyrite (FeS2) and Ni0.1Fe0.9S2 NCs show p-type conductivity while Ni0.2Fe0.8S2 and higher Ni concentration alloys exhibit n-type conductivity. Application of these alloyed NC thin films as the hole transport layer for CdTe solar cells revealed that Ni0.05Fe0.95S2 NCs perform best with the average increase in efficiency of ∼5%, with the best cell performing up to 8% better than the laboratory standard copper/gold (Cu/Au) cell.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...