Electrically/infrared actuated shape memory composites based on a bio-based polyester blend and graphene nanoplatelets and their excellent self-driven ability
Abstract
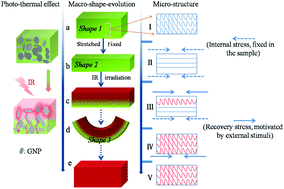
Multi-stimuli-responsive shape memory polymers (SMPs) have a wide range of potential applications in many fields. In this work, novel SMPs with electrically actuated and infrared-actuated shape memory effects (SMEs) have been developed through the incorporation of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) into the poly(caprolactone) (PCL)/polyurethane (PU) blend through a mechanical compounding process. The dispersion of GNPs, the morphology of the blend composites and the crystalline structures of the PCL component were systematically investigated. The results demonstrated that although GNPs did not influence the miscible state of the blend, at a relatively high load they formed a percolated network structure, which apparently influenced the crystalline structure of the PCL component. The electrical resistivity measurements showed that the blend composites had excellent electrical conductivity properties, and the percolation threshold was about 1.62 wt%, which endowed the samples with excellent electrically actuated SMEs. By detection of the variation of the sample surface temperature under the infrared (IR) illumination conditions, the excellent photothermal effect of the blend composites was demonstrated. A largely accelerated shape recovery process under the IR illumination conditions was achieved for the blend composite samples. Specifically, by constructing the oriented structure in the sample and then introducing IR illumination, the sample could accomplish the complex deformation, exhibiting the excellent self-driven ability. The dual-responsive SMEs of the PCL/PU/GNP blend composites endow the material with wide potential applications in many fields, such as smart switches, robot hands and biomedical devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry C HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...