Dimethylsilyl-linked anthracene–pyrene dimers and their efficient triplet–triplet annihilation in organic light emitting diodes†
Abstract
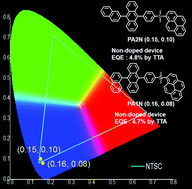
New deep blue emitters containing an sp3-hybridised tetrahedral silicon core with dimethyl groups, 9,10-biarylanthracene, and pyrene were synthesised. The pyrene group, with planar π-conjugation and a slightly larger energy gap than that of anthracene, is expected to work as an intramolecular host group in organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs). Density functional theory (DFT-B3LYP) and time-dependent DFT calculations for molecular orbitals and excited states of pyrene and anthracene units showed the possibility of intramolecular energy transfer and a triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) process. The maximum external quantum efficiencies (EQEs) of non-doped devices using PA1N and PA2N were 4.7% and 4.8%, respectively, while the maximum EQEs of doped devices using PA1N and PA2N as dopants (3 wt%) were 4.5% and 3.6%, respectively. The EQE of the non-doped device with a low photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) (14%) was higher than that of the doped device with a high PLQY (74%), which resulted from the existence of a contribution reproducing radiative S1 excitons from nonradiative T1 excitons in the non-doped devices. Both non-doped and doped devices using PA1N and PA2N showed high color pure blue emission. [Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage coordinates, CIE (x, y), of the non-doped device were (0.16, 0.08) for PA1N and (0.15, 0.10) for PA2N.]


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...