Temperature-dependent reaction between trimethylaluminum and poly(methyl methacrylate) during sequential vapor infiltration: experimental and ab initio analysis
Abstract
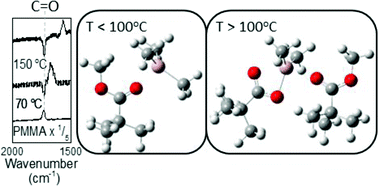
Vapor-phase, metal-containing organic compounds can diffuse into polymers and modify the material composition and structure. In this work, using a sequential vapor infiltration process based on atomic layer deposition chemistry, we combine in situ Fourier transform infrared transmission and quartz crystal microbalance experiments with ab initio quantum chemical modeling analysis to evaluate and identify likely reaction mechanisms when poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) thin films are exposed to trimethylaluminum (TMA) vapor. We find that TMA readily diffuses into the PMMA, where it physisorbs to ester carbonyl units (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) to form a metastable C
O) to form a metastable C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯Al(CH3)3 adduct structure that desorbs at moderate temperatures (<100 °C). The Lewis-acidic TMA withdraws charge from the C
O⋯Al(CH3)3 adduct structure that desorbs at moderate temperatures (<100 °C). The Lewis-acidic TMA withdraws charge from the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, shifting its stretching frequency from 1732 cm−1 in untreated PMMA to 1670 cm−1 after TMA exposure. At higher temperatures IR results show a new feature near 1568 cm−1 that is stable, even upon exposure to water vapor, indicating covalent bond formation. Based on known TMA–polymer reaction mechanisms and ab initio model results, we propose that at T > 100 °C, TMA reacts with PMMA to form covalent resonant C
O, shifting its stretching frequency from 1732 cm−1 in untreated PMMA to 1670 cm−1 after TMA exposure. At higher temperatures IR results show a new feature near 1568 cm−1 that is stable, even upon exposure to water vapor, indicating covalent bond formation. Based on known TMA–polymer reaction mechanisms and ab initio model results, we propose that at T > 100 °C, TMA reacts with PMMA to form covalent resonant C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O⋯Al–O–C bonding units, and does not form –O–C–O–Al(CH3) as previously hypothesized. This mechanistic insight will help elucidate other polymer/Lewis-acid vapor reactions and could enable new applications for sequential vapor infiltration processes.
O⋯Al–O–C bonding units, and does not form –O–C–O–Al(CH3) as previously hypothesized. This mechanistic insight will help elucidate other polymer/Lewis-acid vapor reactions and could enable new applications for sequential vapor infiltration processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...