Mechanically tough double-network hydrogels with high electronic conductivity
Abstract
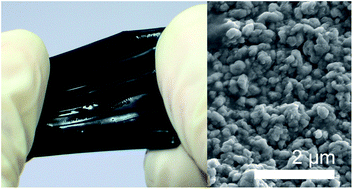
New, mechanically tough, and electro-conductive double-network hydrogels (E-DN gels) were synthesised by oxidative polymerisation of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene in ethanol in the presence of a double-network hydrogel (DN gel) matrix composed of poly(styrenesulphonic acid) as the first network and poly(N,N-dimethyl acrylamide) as the second network. The E-DN gels showed not only excellent mechanical performance, with a Young's modulus of 3 MPa and a fracture stress of 2 MPa, but also electrical conductivity of the order of 1 S cm−1 in both dry and water-swollen states. Scanning electron and atomic force microscopy observations showed that electro-conductive poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) particles with diameters of several hundred nanometres uniformly filled the interior of E-DN gels. The AC impedance analysis clearly indicated that the E-DN hydrogels were simple resistors that became charge carriers as a result of PEDOT doping. Even when the E-DN gels were swollen and had high water content, the electrical conductivity resulted from electronic carrier transport.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...